
The destination: Curlew National Grassland. The mission: Find a Monarch. The crew: your favorite CLM interns (plus a few guests).

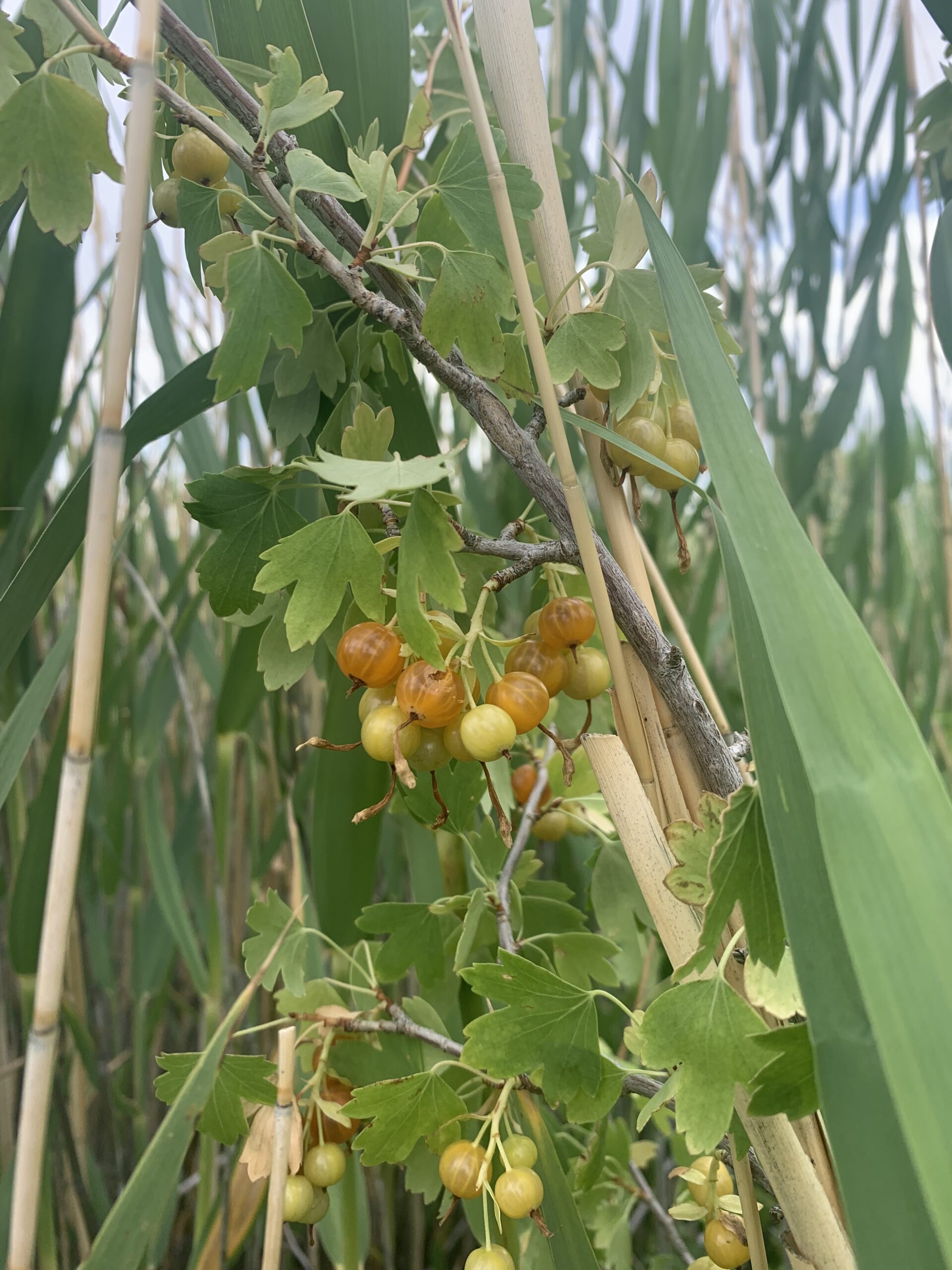
As soon as we parked our trucks in the Twin Springs campground on the Curlew, I knew we were in for a good day. Alex and I were joined by our mentor, Rose, one of the botany interns, Carson, and an archaeologist, Ashley. We were waiting to meet up with the rest of our group for the day (a collection of NRCS, rec, and range people) when we noticed an absolutely massive population of Ribes aureum. If you’re unfamiliar, Ribes aureum (or Golden Currant) is a delicious native shrub, and it was out in full force. We quickly decided that it was time for our first opportunistic collection, and within moments everyone had a paper bag in hand and was carefully picking berries off of every plant in sight. The abundance was awe inspiring after months of waiting for a seed collection to complete, and the morning snack was much appreciated. About a half hour into our collection, Derek from the NRCS Plant Materials Center in Aberdeen, ID, showed us how the pros do it- racket in hand with a custom built canvas collection bag. Within mere seconds, he had out collected all of us combined.

While the Ribes collection was a great start to the day, it was not our objective for the day. We were all assembled to participate in the Monarch Bioblitz, a community effort across North America to collect data on Monarch populations. We were heading to a few known sites of Asclepias speciosa in order to look for monarch eggs, caterpillars, and adults.
Within minutes at our first site, we had spotted an adult monarch. An extensive survey of the milkweed in the area revealed many more of the beautiful iridescent eggs. Monarchs have a few distinct look alike species, but luckily none of the species that have visually similar eggs had a range that extended as far north as Idaho. Below are a few of the most common look alike species for Monarchs. While the Queen’s and Soldier butterflies have very similar eggs and larvae, the range does not extend to where we were surveying- that made life easier! The Viceroy adults are very similar in appearance to Monarchs, which can cause confusion, but if you look carefully you can see a distinct horizontal line on the Viceroy wings that is missing on Monarchs. Monarchs will also have a much slower flight pattern (flap-flap-gliiiide) while Viceroy has a much faster and more erratic flight pattern. These key differences are very important to note during surveys!

The bright colors of monarch caterpillars and butterflies indicates to predators that they are not a great choice of meal… Because Monarch caterpillars exclusively feed on milkweed, they are full of a toxin called cardiac glycoside, which stops the sodium pumps in the bodies of predators that aren’t adapted to the chemical. Because of this defense, many species have evolved to mimic the bright patterns of the Monarch, despite not being toxic themselves!



At our second site, we finally got to put our butterfly nets into action. For first time catchers, we quickly learned that capturing butterflies is a LOT harder than it sounds. After tromping through a creek and many pricker filled plants, Cheryl used her bug catching skills to capture our first adult male monarch and demonstrated her superior butterfly catching form. Although we didn’t plan on tagging the butterflies we surveyed that day, we did take the opportunity of this first male to learn how to properly place the tag.
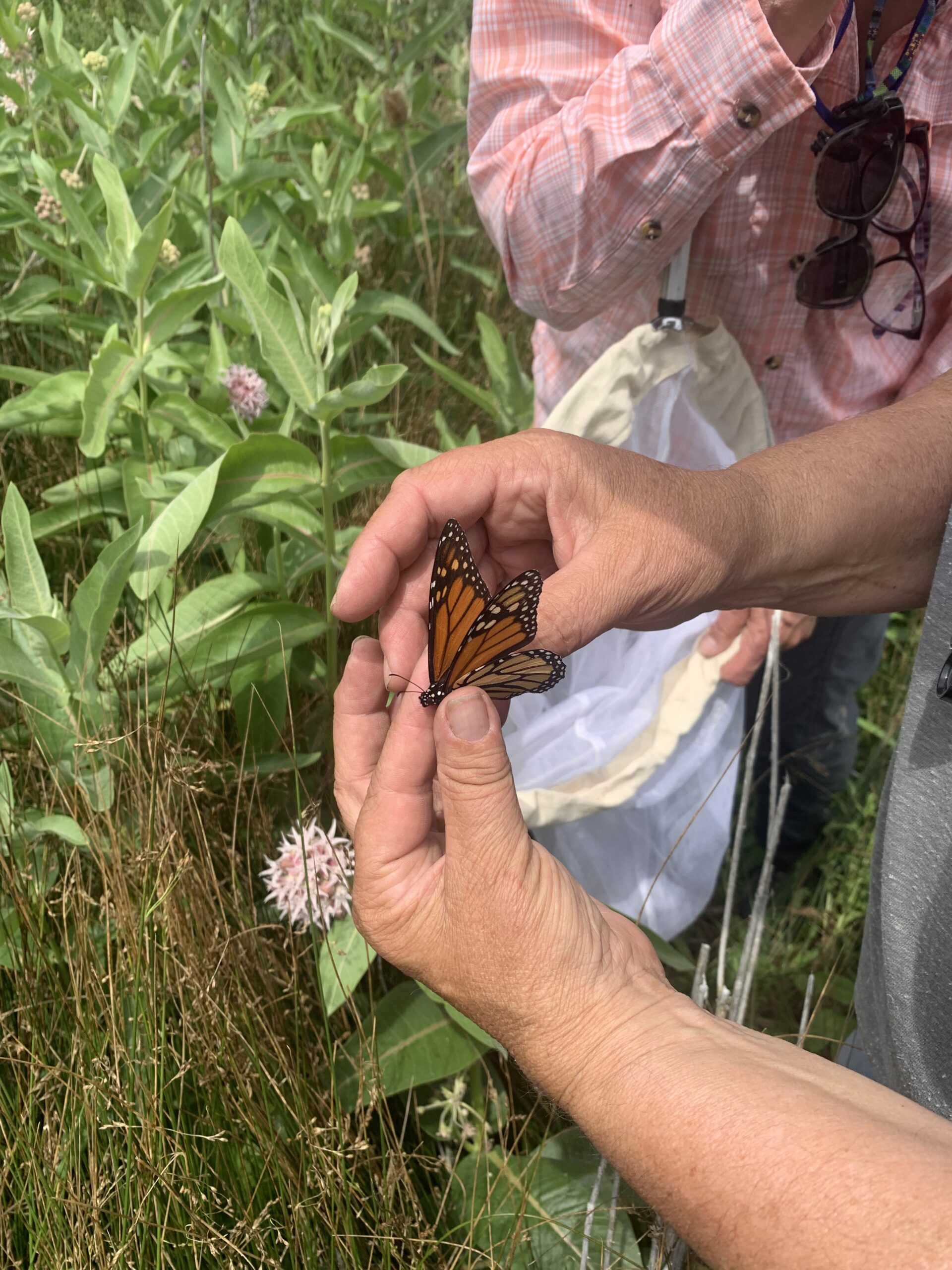
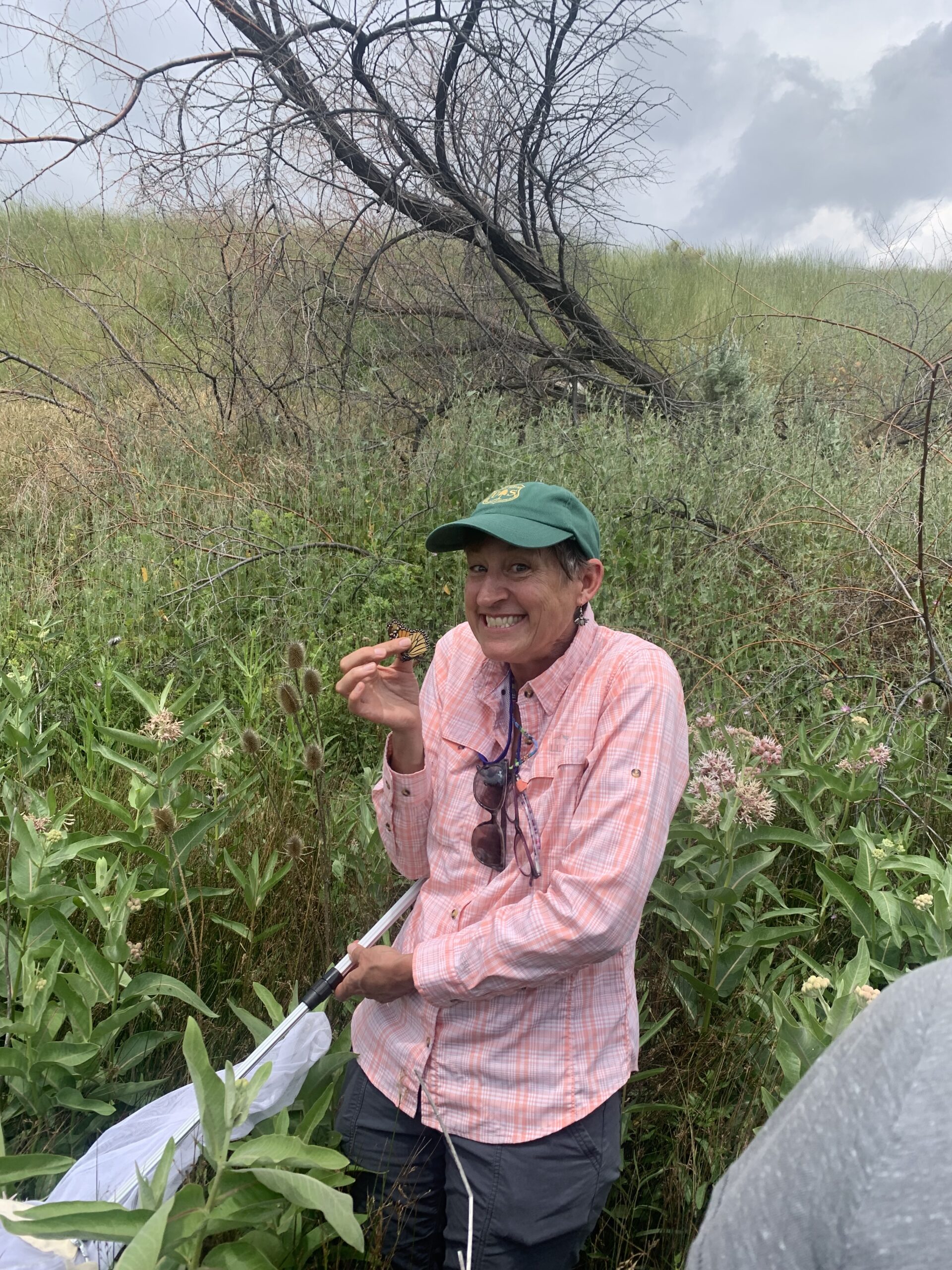


By the time we reached our third site, we had already surveyed around thirty monarchs. This site once again blessed us with a population of Ribes, which provided us a much needed snack. Although some of us (okay, maybe just me) got a little carried away with the berry foraging and forgot to look for butterflies, we did find two monarch caterpillars.
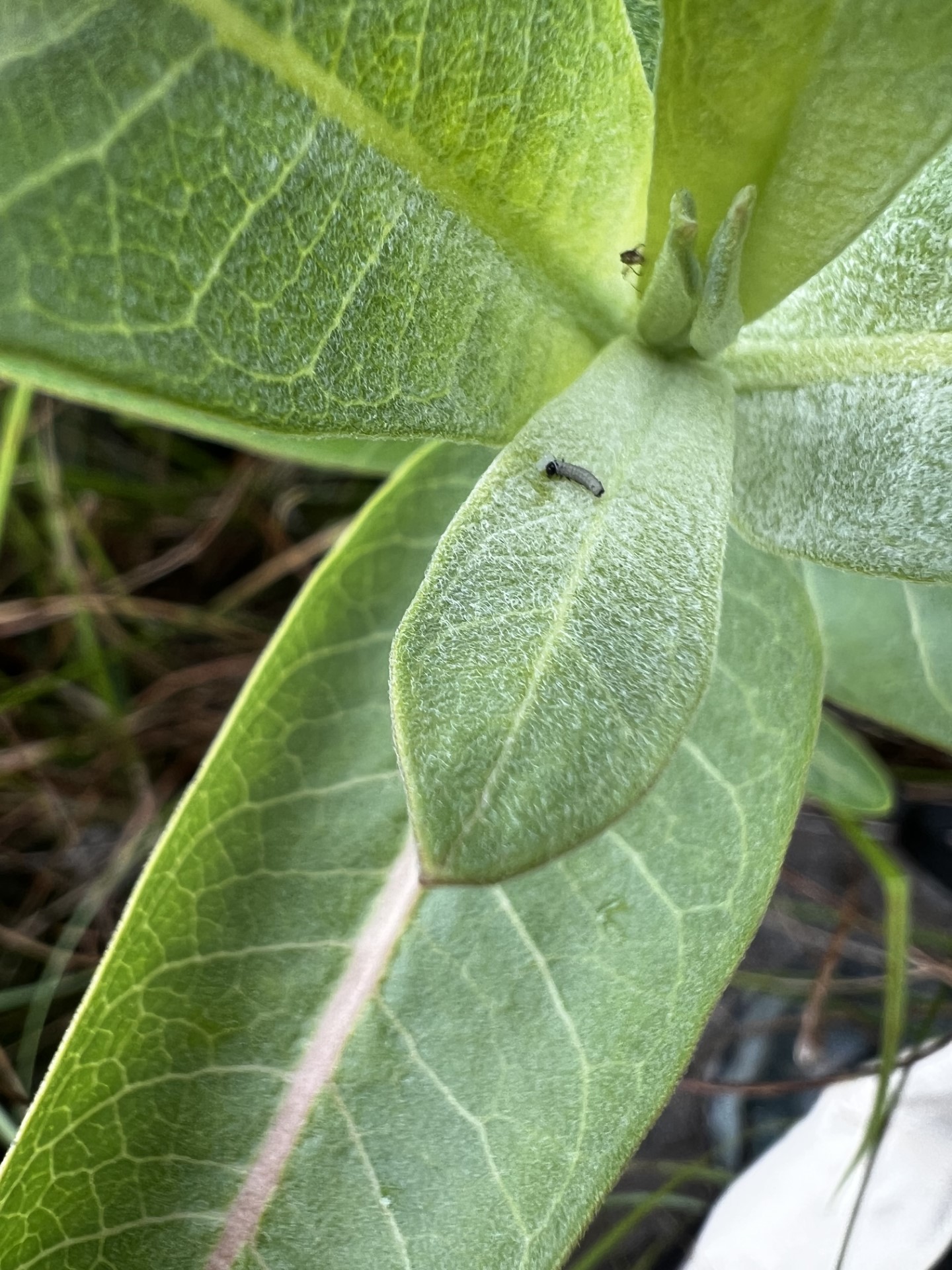
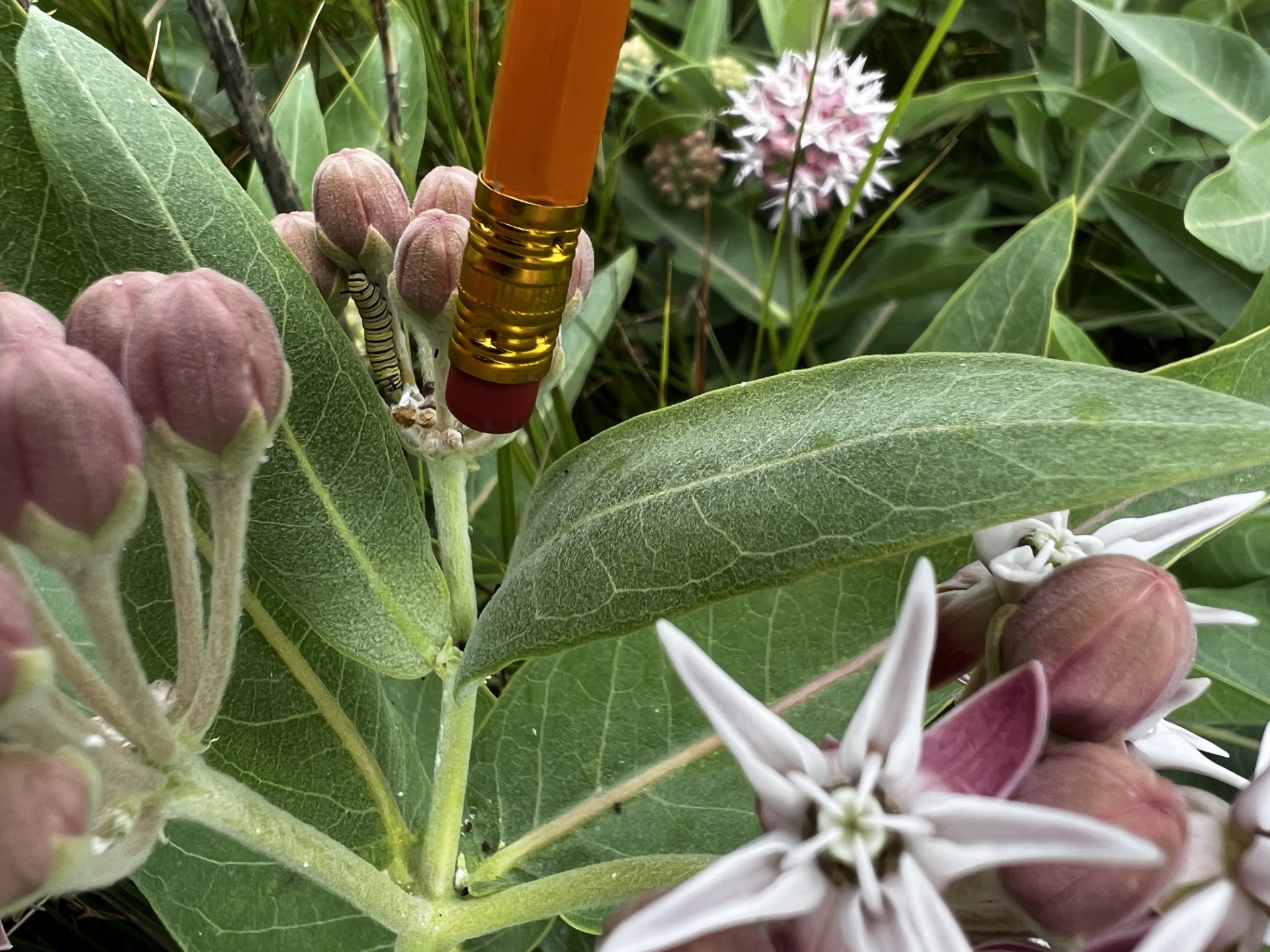
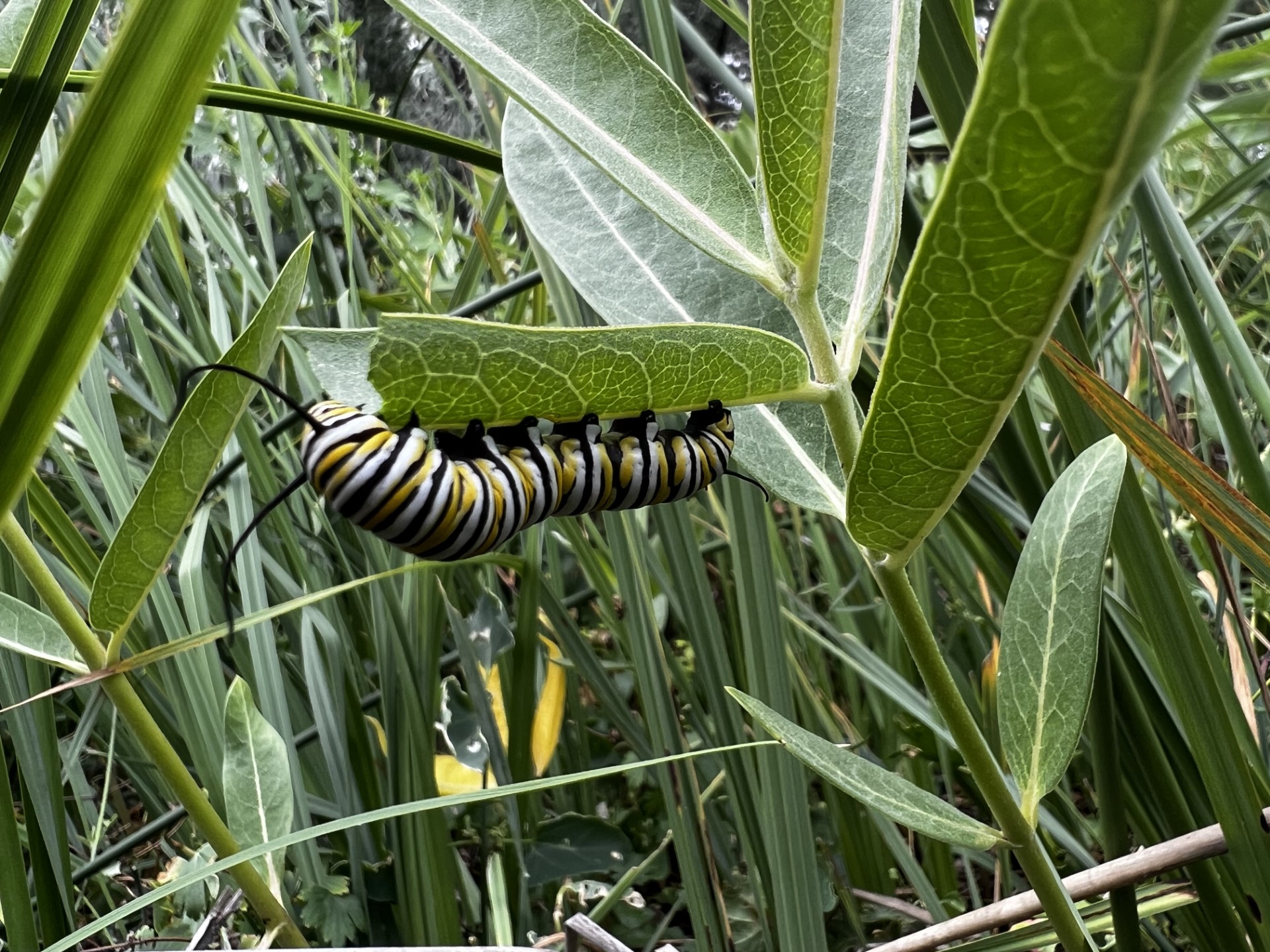
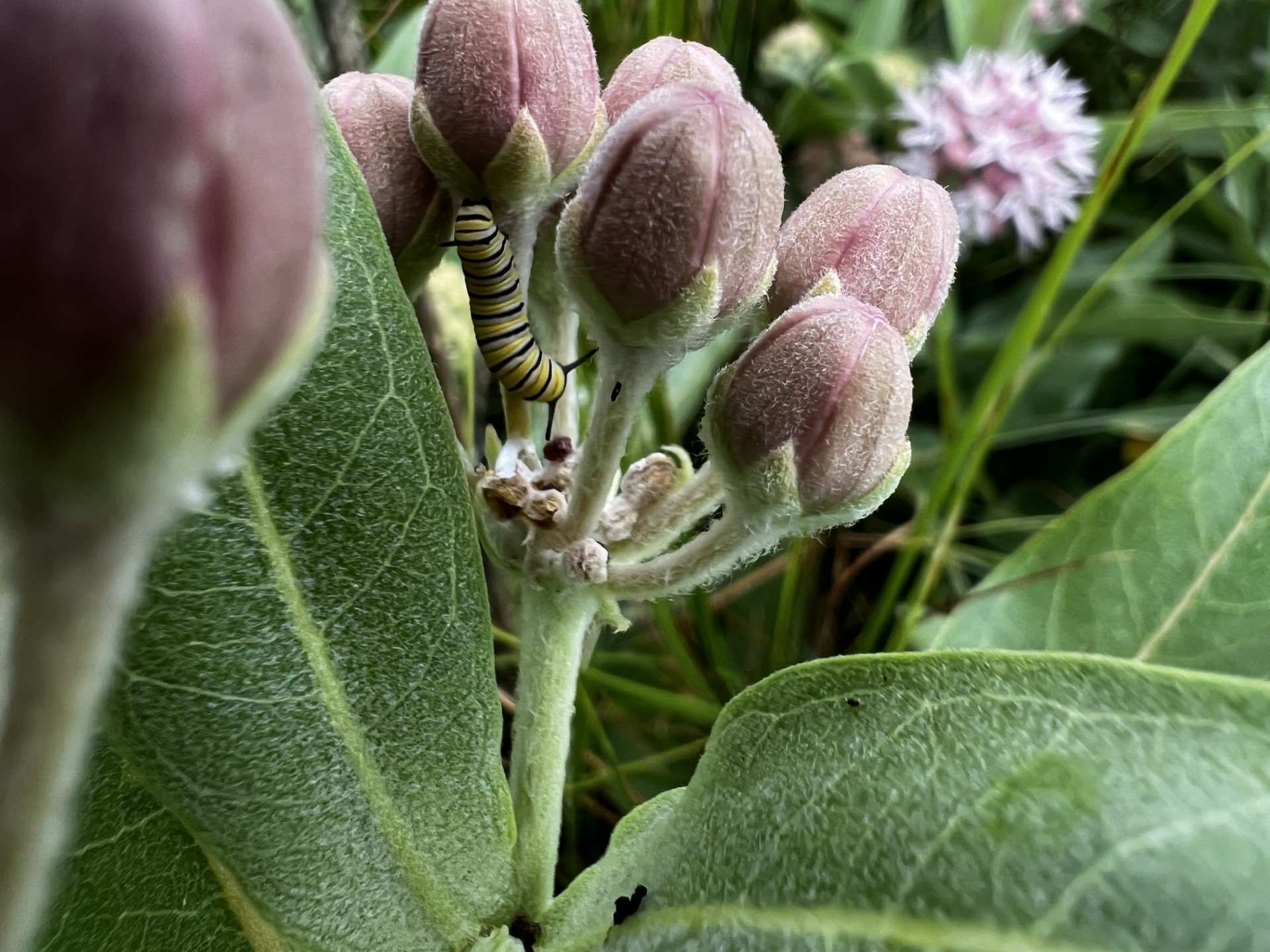




Caterpillars are classified into five different instars based on their development. The stages can be a matter of days apart and are determined by visual cues like banding or presence of spots. The instar stage was a hot debate every time a caterpillar was spotted, until we remembered the handy monarch guides that we had which described in detail several key differences between each stage. Go us for preparedness!
So- Mission accomplished! We had a very successful survey of various milkweed populations, and are expecting to see the monarchs flourishing when we go survey again in a few weeks. Because monarchs are an endangered species, understanding the health of our populations is of extreme importance across North America! p.s. if you made it this far, enjoy the demonstration on how not to catch a monarch 🙂
If interested, there are a lot of great resources for monarch biology, habitat, and monitoring efforts at these sources:
