As I write this, the first snow of the year is falling outside. I’m sitting near the window of a coffee shop, watching the flakes swirl before melting on the wet pavement. Almost all the trees have lost their leaves now, and, in the mornings, there is frost before there is dew. It’s hard to believe this is my last blog post, but it also feels like field work is coming to its natural conclusion here in the Northwoods. Once again, the season is changing. In the meantime, though, there’s still much to do — projects to finish, harvests to reap, and preparations to make for the snow that will not melt when it hits the pavement.
It’s amazing how quickly the chill descended. We were lucky to have a long early-fall full of 70 degree weather and brightly colored leaves. My co-intern Tessa and I spent many days out in the forest treating invasive honeysuckle and buckthorn. I learned that in the fall you have to be particularly careful where you set down your tools because it doesn’t take much for them to get buried in a pile of leaves never to be seen again.
Throughout our internship at Ottawa National Forest, Tessa and I have gotten a chance to spend time with many different branches of the Forest Service, from marking trees with timber specialists to working on turtle conservation with wildlife technicians. Plants and animals aren’t the only creatures in the forest though. The Ottawa’s almost a million acres draws in people too. Recreation crews work hard to make sure the forest can be enjoyed by all. On Tuesday this week, Tessa and I got a chance to be a part of that, traveling to Black River Harbor to help out recreation team members Joe and Ali.
Black River Harbor is home to the Ottawa’s only Lake Superior shore line. It is also one of the most gorgeous places I have ever been. A giant suspension bridge crosses the rushing Black River, swaying in the wind just enough to make you nervous (even though you’re perfectly safe). The bridge leads to an expansive sandy beach with stones worn smooth by a lake so big other lakes think it must be the ocean. All summer, the shore is packed with people playing in the waves, building sandcastles, skipping rocks, and constricting a massive driftwood lean-to that has not yet toppled in the breeze.
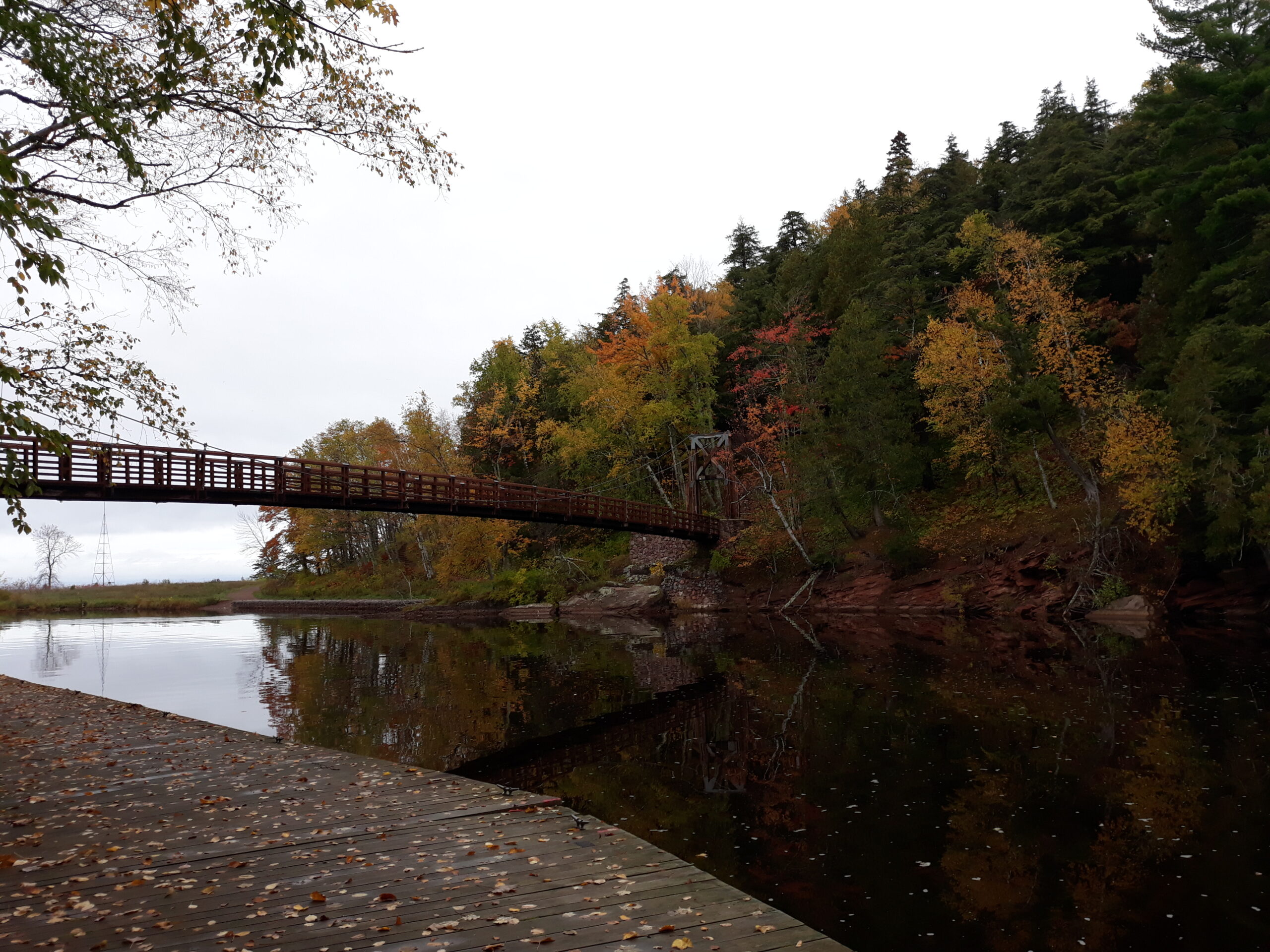

This is where the Ottawa’s recreation team shines. Whether it’s answering questions or saving the day with a truck bed full of toilet paper, they’re the face of the Forest Service and help ensure that the Ottawa’s wide swaths of public land are easily accessed and enjoyed by the very people they’re meant for, the public.
When we arrived at the harbor our first stop was the campground’s water building, or, more accurately, a small patch of trees right next to the water building. The campground has shut down for the season, so it’s a great time to do maintenance work there. After gathering around the truck to review the day’s safety considerations, Joe took Tessa and I a few dozen feet into the trees. We stopped at a tall aspen with a significant lean. Joe brushed aside some leaves and showed us a patch of raised ground at the base of the tree. That raise, he explained, was the root stock of the aspen ripping slowly but surely out of the earth. Joe, an experienced feller, would be taking the tree down to ensure the safety of the water building and more importantly the many campground visitors.
In order to take down the leaning aspen, two smaller aspen would also have to be cut, this would leave a clear path for the larger tree to fall. Joe explained that before any tree is cut there should be at least two clear paths for the sawyer (a fancy word for tree cutter) to enable a quick retreat without obstacles to slow them down or trip them up.
We helped clear logs and brush until the way was unobstructed. Then, Joe hit the tree with the dull side of a hatchet. A low “Thunk!… Thunk!… Thunk!” rang through the empty campground. That was good; The tree sounded solid and not rotten in the middle. Then, Tessa, Ali, and I got a safe distance away and put our ear plugs in.
As we watched Joe take down the trees, Ali explained to us some of the many intricacies of felling. Everything from the height of the tree, to the lean, to the species should be taken into consideration. There are almost as many different approaches to cutting a tree as there are scenarios you might encounter, and an experienced sawyer will be able to determine what they are working with and pick the right strategy for the job.
While Ali and Joe began cutting the freshly fallen trees into firewood, Tessa and I set out on our task for the day. We strapped leaf blowers onto our backs and went campsite to campsite clearing out a thick mat of freshly fallen leaves. I was surprised at how physically demanding the work was. Directing the leafblower forward felt like walking against a strong wind, probably because, in a roundabout way, that’s what it was. One by one we cleared the campsites, leaving them ready for visitors in the spring and eliminating the falling risk that comes with a blanket of slippery, decaying leaves.
I’ve been to many campsites, but I never stopped to consider how they are maintained. It always felt to me that they simply existed just as I encountered them, but did not grow and change like a forest does. Spending time with Joe and Ali showed me that they do grow and change and, just like the forest as a whole, benefit from being thoughtfully managed.
Our work at the campground on that chilly fall day reminded me of planting daffodil bulbs with my dad as a child. When the world was growing cold, we would tuck the bulbs safe beneath the soil. Nothing would happen for a long time. Finally, many months later when I had forgotten we ever planted flowers at all, green shoots would break through the last snowfall of the year. I won’t be around in the spring when the snow melts from the Black River Harbor campsites, but the work we did this fall will be there to greet the campsites’ first visitors.
—
On a Friday morning, I scarfed down a bowl of oatmeal, threw some dried apricots in my lunchbox, and grabbed a blaze orange hat, before driving the short drive to the Ottawa’s Ironwood office. There, I met with Tessa and forest botanists Sue and Katherine. The morning was bright and crisp as we set out together into the field. Our mission for the day was to collect seeds from Ottawa’s native flowers for Project Wingspan.
Project Wingspan is an initiative supported by well over a dozen ecologically-minded partner organizations that have come together with the goal of increasing pollinator habitat in the Great Lakes region and broader midwest. One of the best ways to accomplish that goal is by propagating the native flowers that provide food and shelter for so many different pollen-minded friends. Seeds for the project are collected by specially trained naturalists all over the region, and, under Sue’s expert supervision, Tessa and I got to help.
After almost an hour of driving, we pulled up to a promising seed collection spot along the roadway. All year, various Forest Service field-goers recorded spots where they saw large populations of native flowers blooming. Now, those flowers have faded, but each location holds thousands of native seeds.
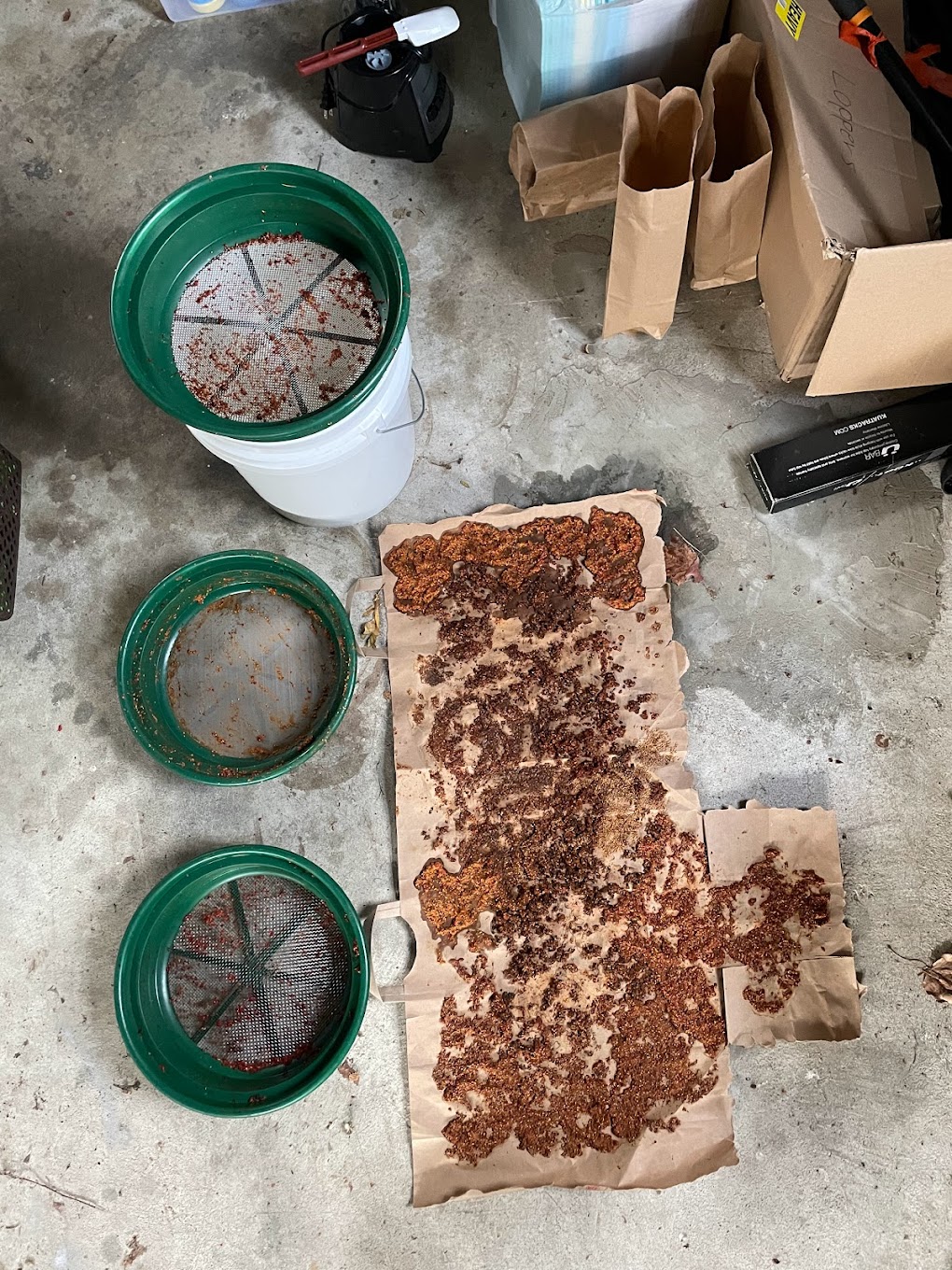
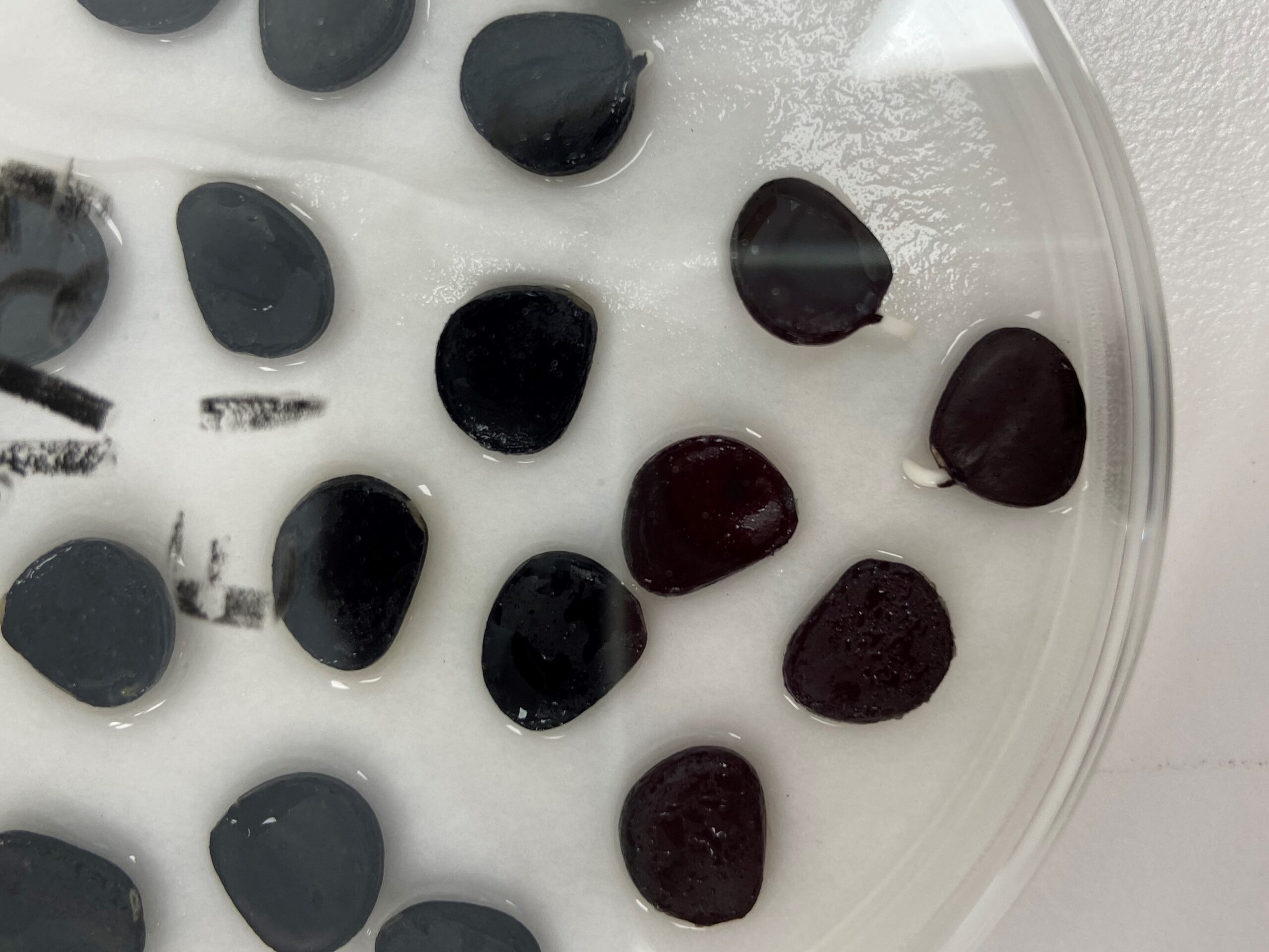
We walked along the road cutting off the spiky seed-heads of black-eyed Susan (Rudbeckia hirta) and watching them fall into our brown paper bags. We were careful not to take too many seeds so that there are plenty left to keep the population healthy. After walking up and down the road, we pooled our collections in a big bag, labeled it, and stored it safely in the truck.
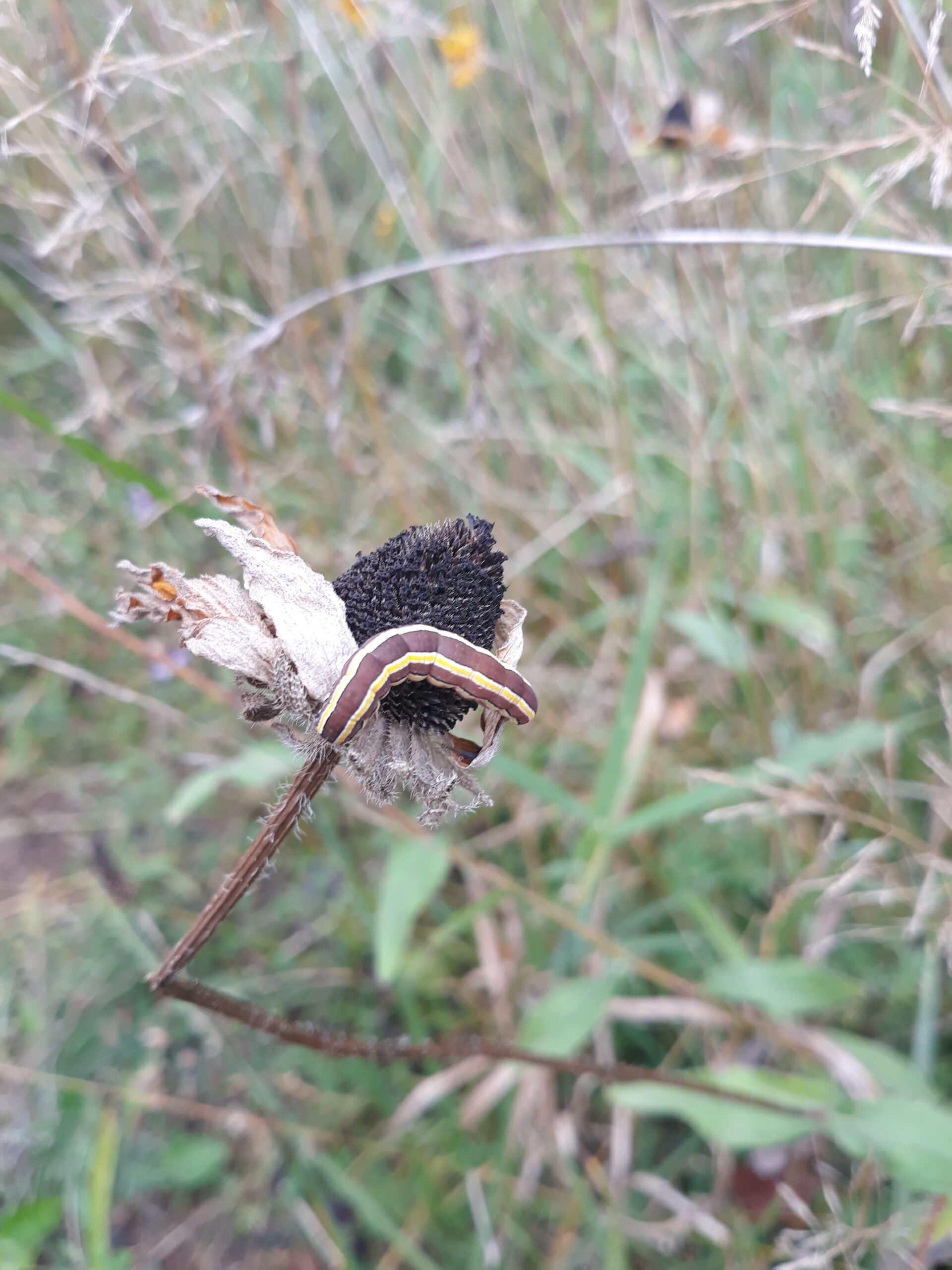

Next, we set our sights on grass-leaved goldenrod (Euthamia graminifolia). The seed-heads were much smaller on the goldenrod than the black-eyed Susan, so, if you got your thumb at just the right angle, you could brush many of them into your waiting paper bag at once. We made sure not to collect seeds from any of the flower’s many doppelgangers and avoided collecting from plants overshadowed by their taller cousins, lest unwelcome seeds drift into our bags to contaminate the bunch. The sun came out as we searched for plants and I held my hands high, warming them before bending down again to continue collecting.
By the end of the day we had big bags of seed from a motley medley of native flowers. We took the carefully labeled bags back to the office and laid them out to dry in tin foil pans scavenged through the years from office potlucks. Over the last few weeks the conference room has slowly been taken over with all sorts of native seeds. A note on the table explains what’s going on and asks guests to “pardon the spiders.”
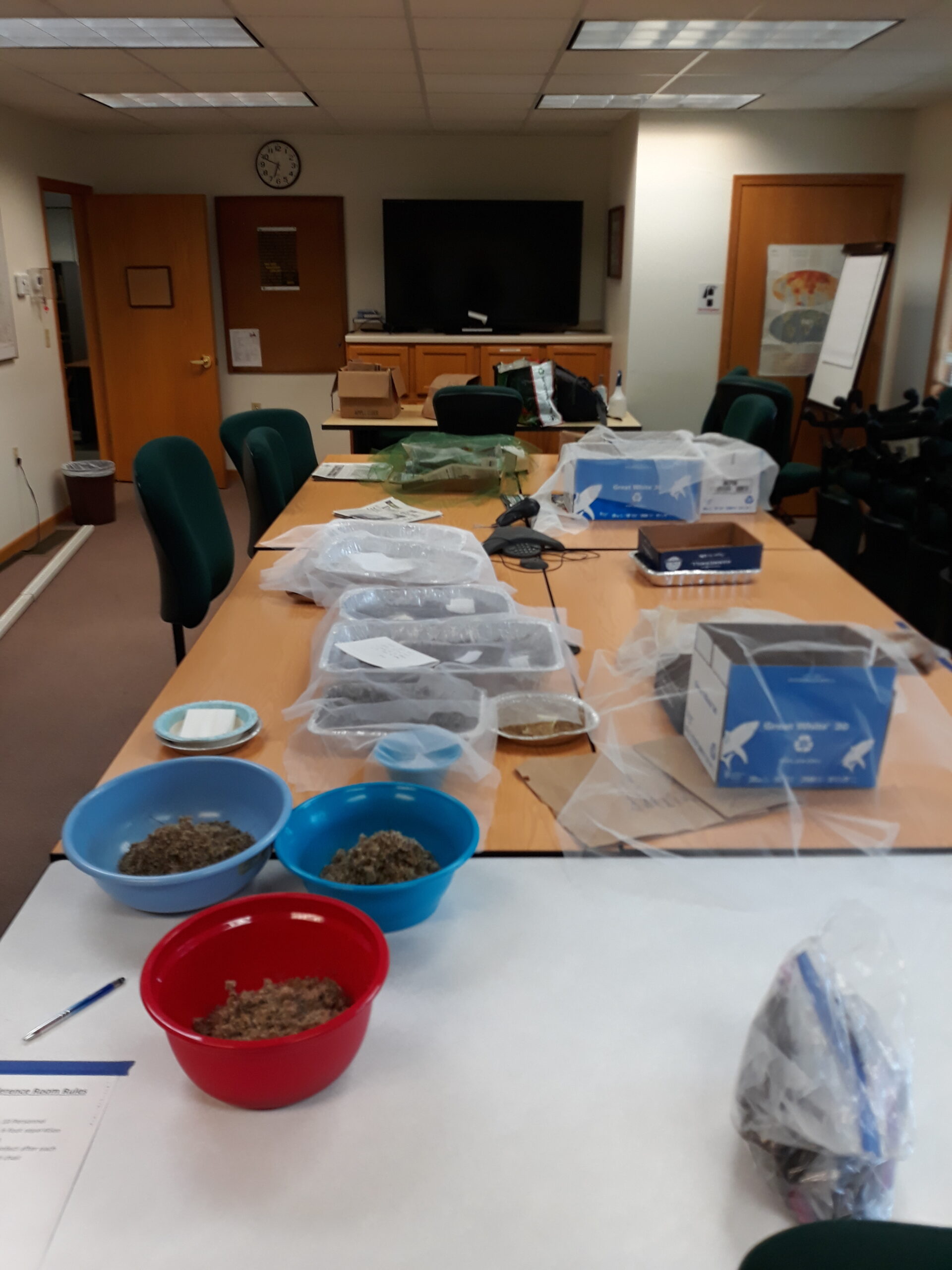

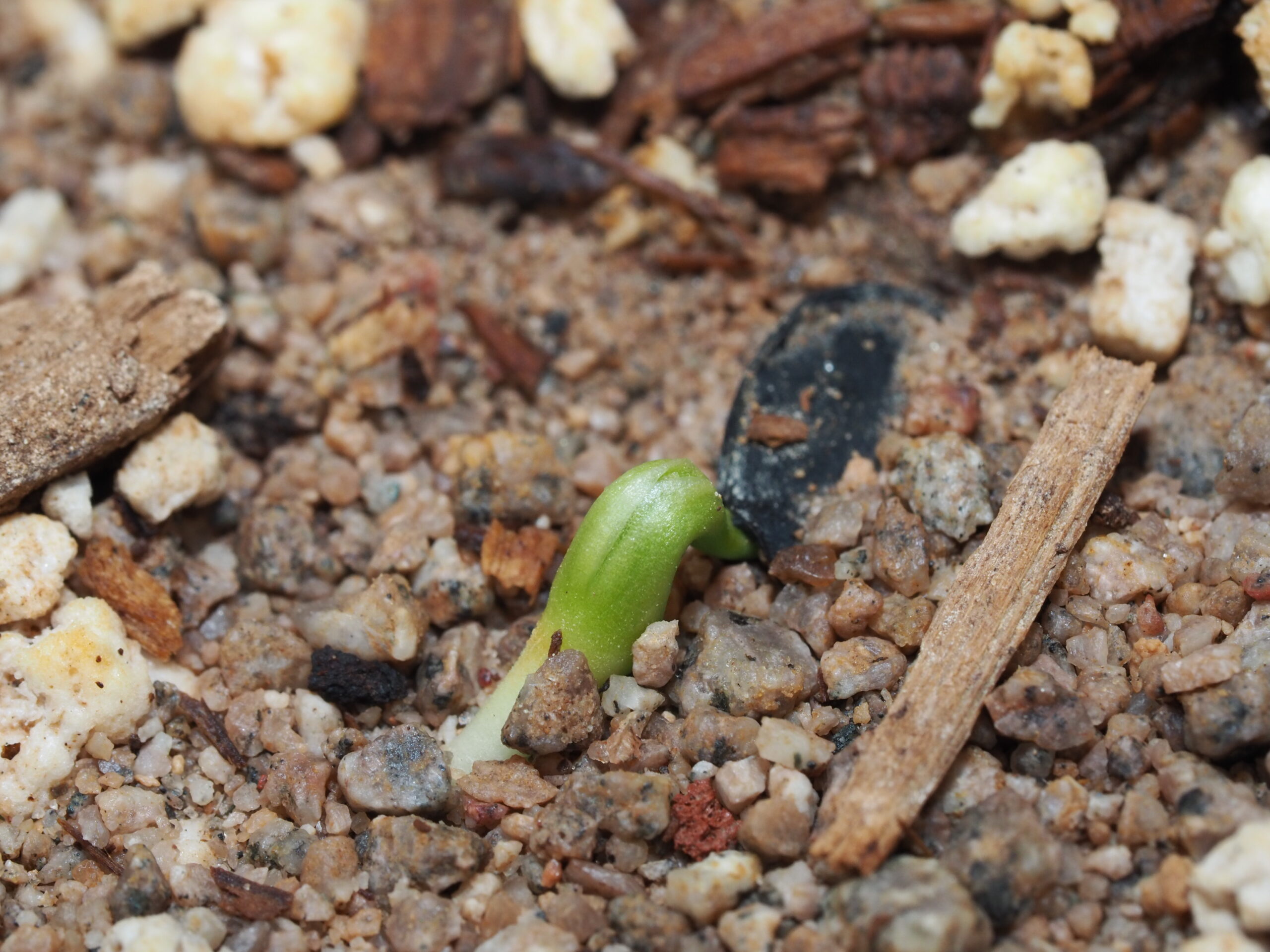
Looking out over the tables laden with small and large seeds, brown and black seeds, smooth and spiky seeds, and everything in between, I couldn’t help, but wonder about their future. Maybe the seeds will end up in a garden, maybe they’ll be planted in a forest or near a school. Wherever they end up, I hope they germinate, take root, and make a home.
—
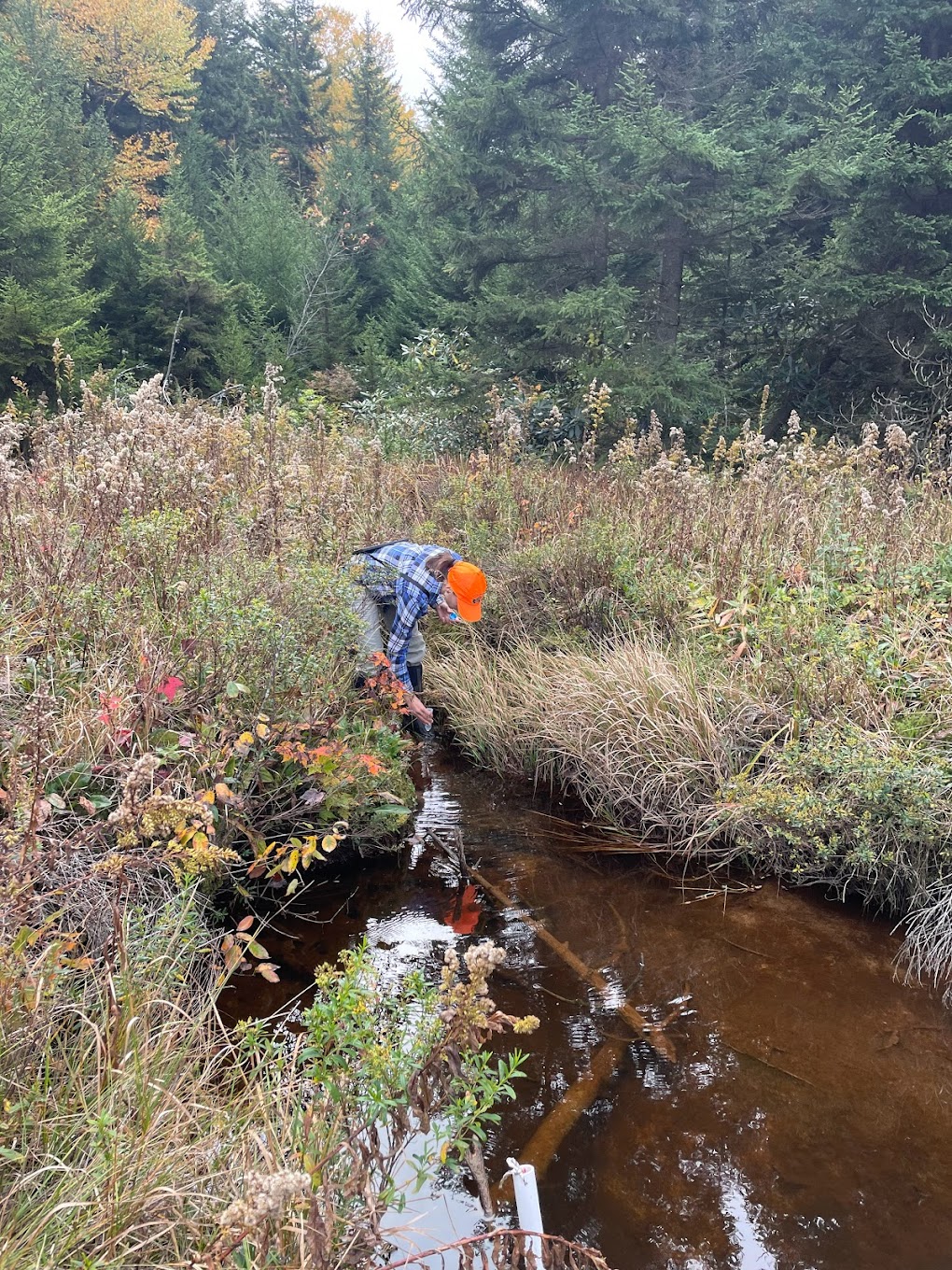
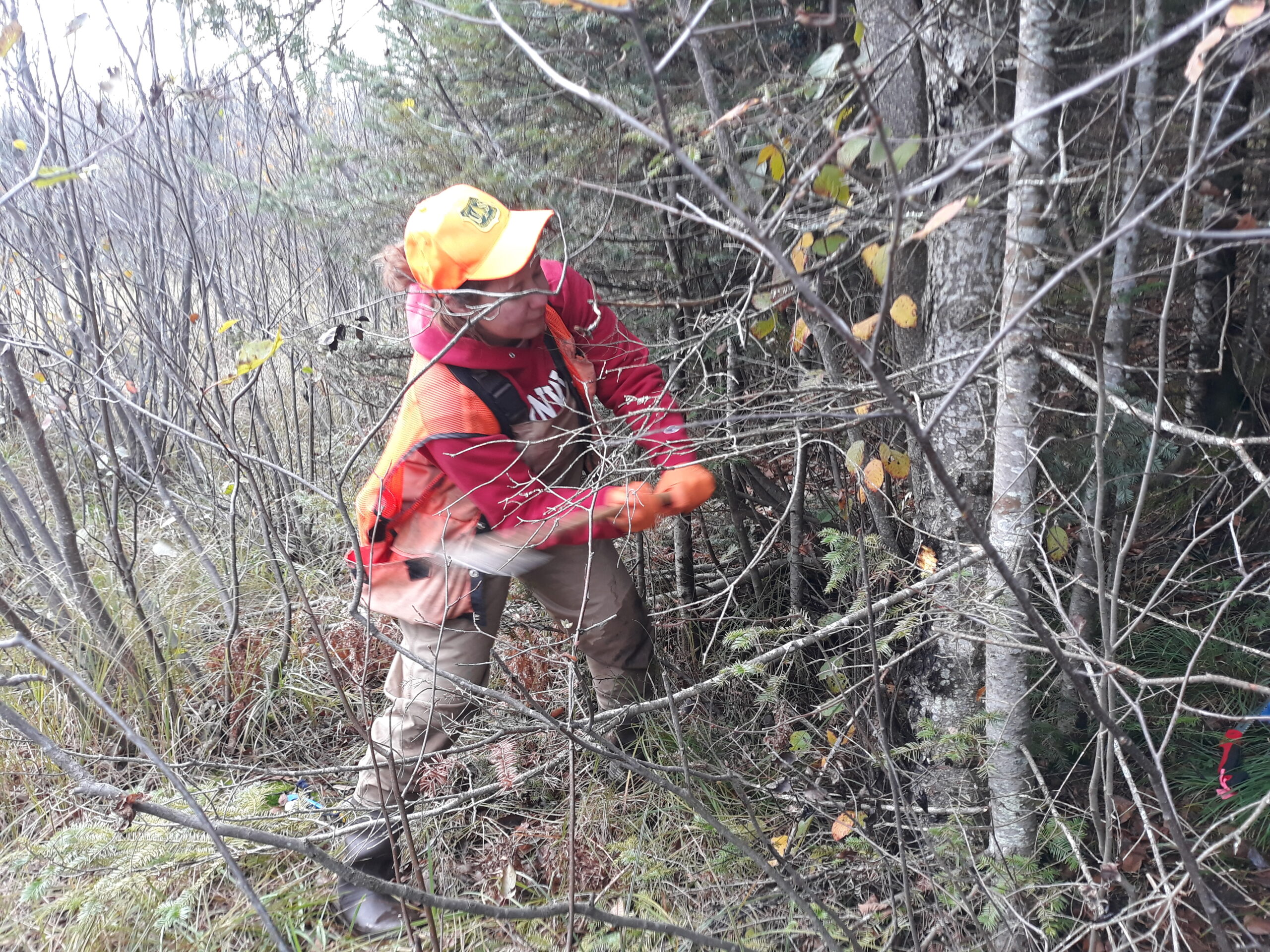
Yesterday, Tessa and I headed to Trout Creek to wrap up work on a weed site that’s been on my mind for most of the fall. In September, Tessa and I discovered the largest invasive buckthorn either of us had ever seen. At almost thirty feet tall, it towered over its numerous descendants. We called it the mother buckthorn. The day we found it, we had neither the time nor tools to treat the giantess, so yesterday we returned with hatchets slung over our shoulders and the whole day ahead of us.
The weather promised that winter is near, but thankfully waders help keep you warm as well as dry. We navigated through tall, dry shore grasses and crossed logs partially-submerged in the frigid water, cutting and applying pesticide to invasive honeysuckle as we went. Finally, the honeysuckle transitioned into knee-high glossy buckthorn, then shoulder-high buckthorn. When we were regularly finding 12 ft tall buckthorn we knew we were close. I looked up, scanning the tree line and there it was, red leaves stark against the bleak, late-fall surroundings.
Tessa and I took turns swinging our hatchets into the base of the mother buckthorn, slowly circling the tree until we had stripped the bark all the way around. I was surprised to find the inner bark was a lovely red-purple color. That’s the thing about invasive species. They are almost all charming which often is why they were introduced in the first place. The problem comes when they spread out of flower gardens and nurseries, bringing economic or ecological harm, often both.

When we finished treating the mother buckthorn the marsh felt strangely still. There was no crash like when Joe cut down the aspen. Unless you looked closely, you might not have noticed anything changed at all. That’s okay, though, because I know something did happen.
That’s how conservation works I think, planting seeds you might not be around to see grow, collecting seeds to be planted far away, or, in this case stopping new seeds from ever falling to reach the ground. To work in forestry is to work on the vast scale of the forest. Some things happen fast, a tree falls. Some things happen slowly, a tree grows. We can do nothing but accommodate.
As part of the CLM program, I’ve gotten to be part of so many projects that were going on long before I arrived and will continue into the future. I had the opportunity to learn from people all over the Ottawa and help them in their work. Figuratively and often literally I was given a chance to plant seeds in a forest I have grown to love. I’m so grateful for all the wonderful people I met along the way who care diligently for the land and let me be a part of that.
As I look back at my time on the forest, I realize that I took seeds with me too, a love of the outdoors that only grew, a greater understanding of federal lands, a heightened awareness of the world around me, and a deep appreciation for land management practices big and small. Even as time goes on and I continue down my professional path, I am sure that I will continue to discover lessons and skills I picked up without noticing like burrs on my sleeve, the beginnings of questions that are the beginning of quests, bulbs that are lying dormant and waiting for spring.