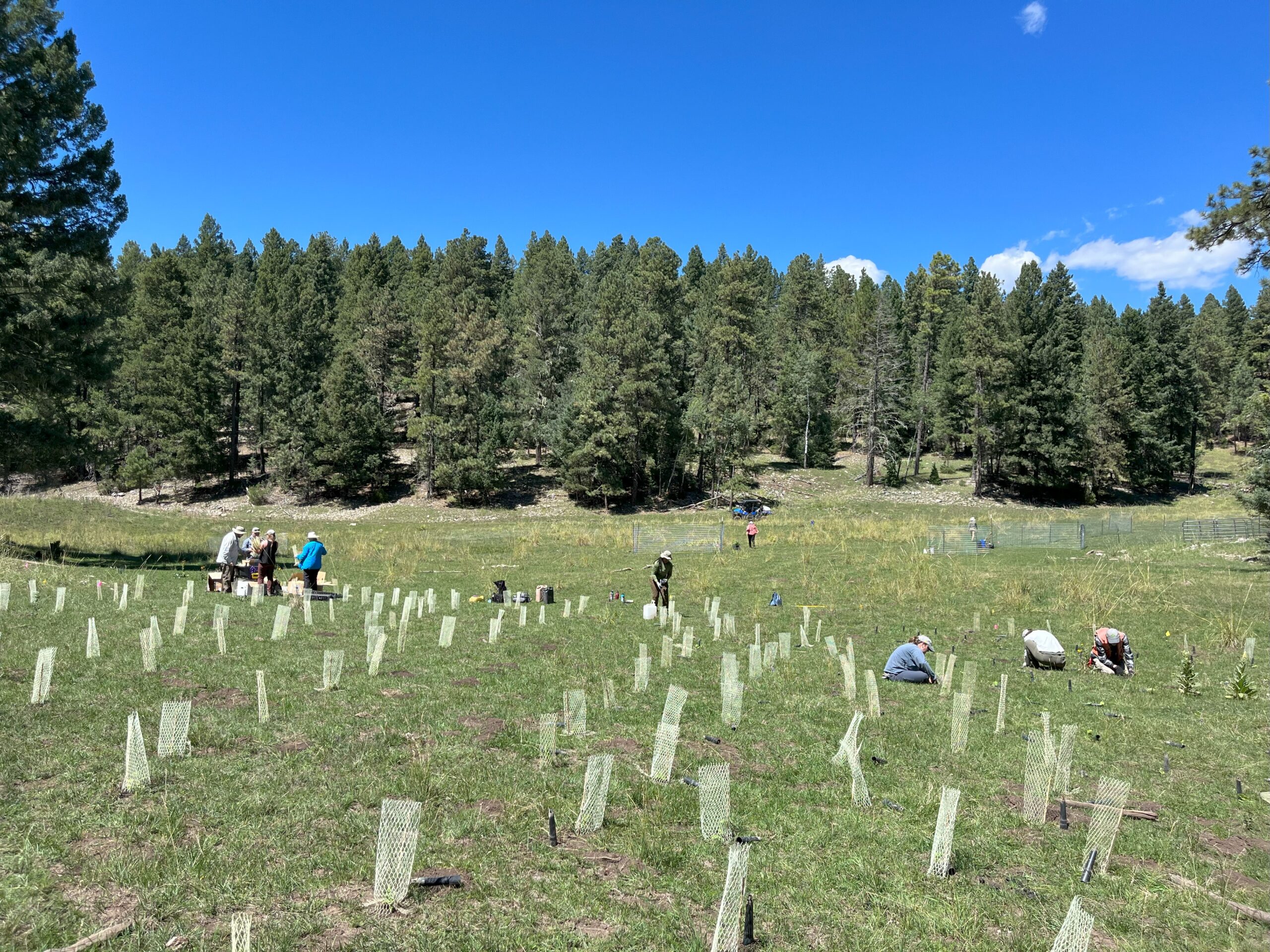
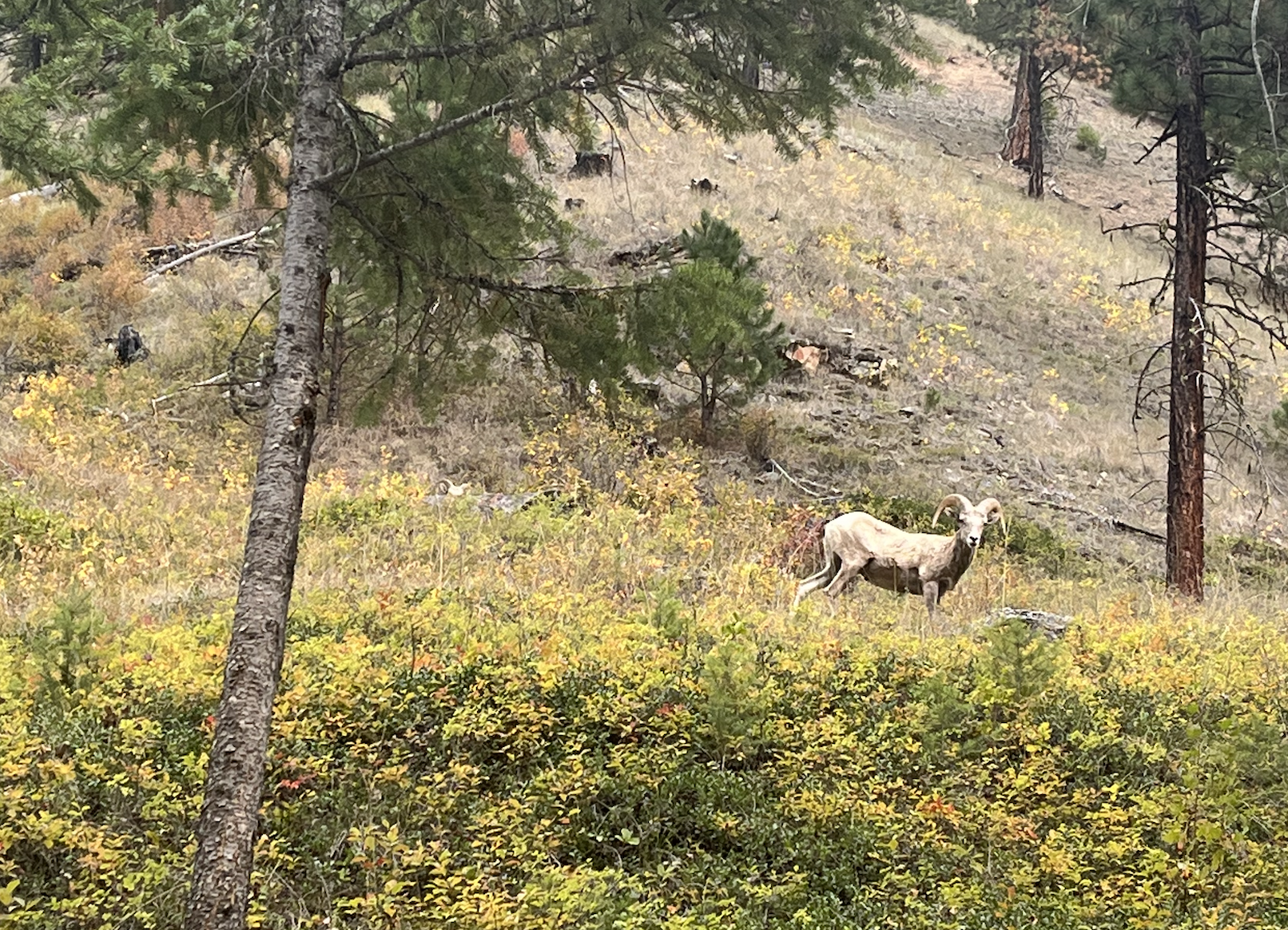
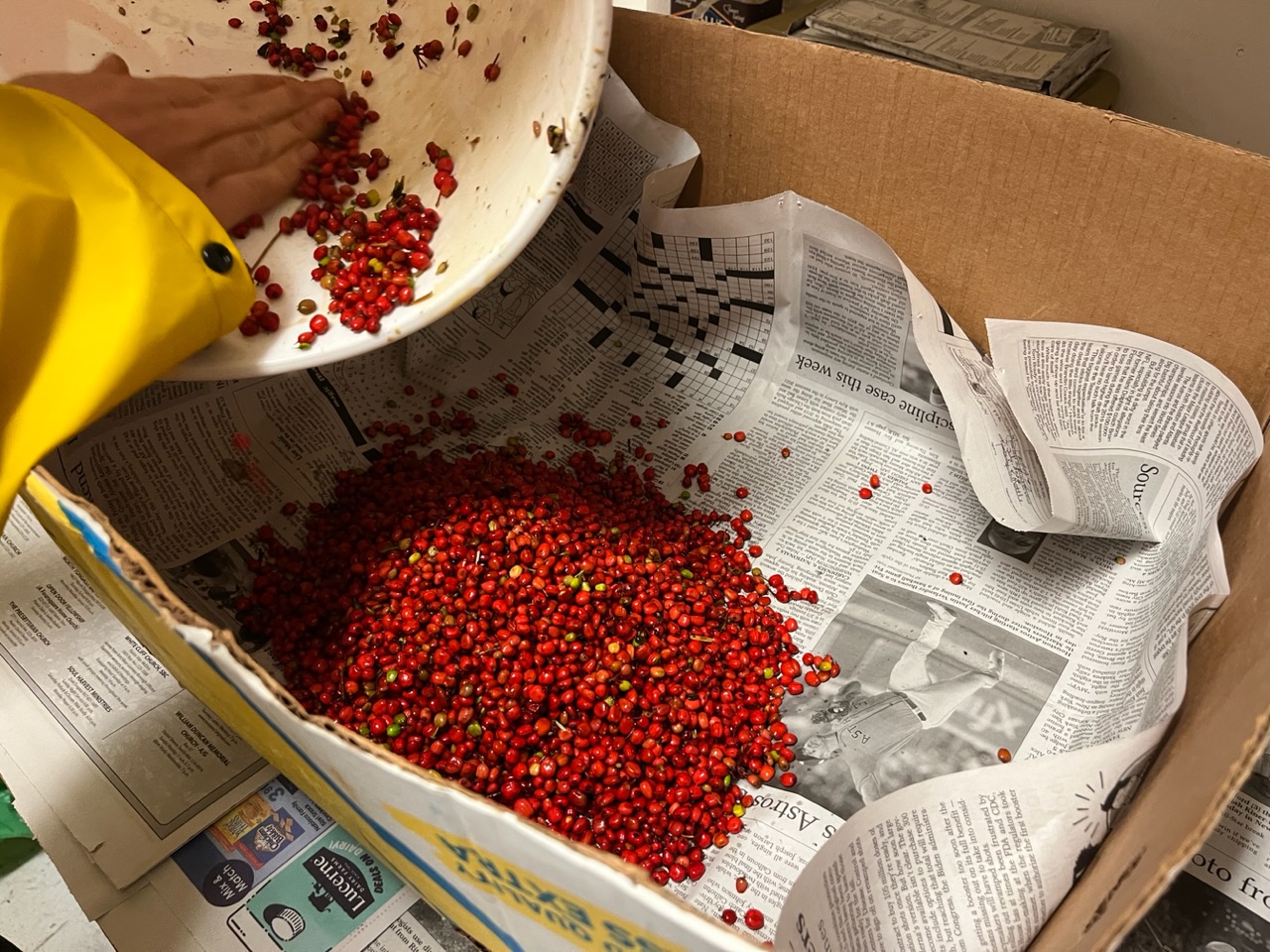
This season the Diamond Lake Botany Crew and I collected a little bit less than 300lbs of fruit! We plan on taking our first trip to the Bend Seed Extractory this Thursday (9/28) to deliver our collections for cleaning. Our collections included Sambucus cerulea (Blue elderberry), Prunus emarginata (Bitter cherry), Rubus parviflorus (Thimbleberry), and Sorbus scopulina (Mountain ash)…
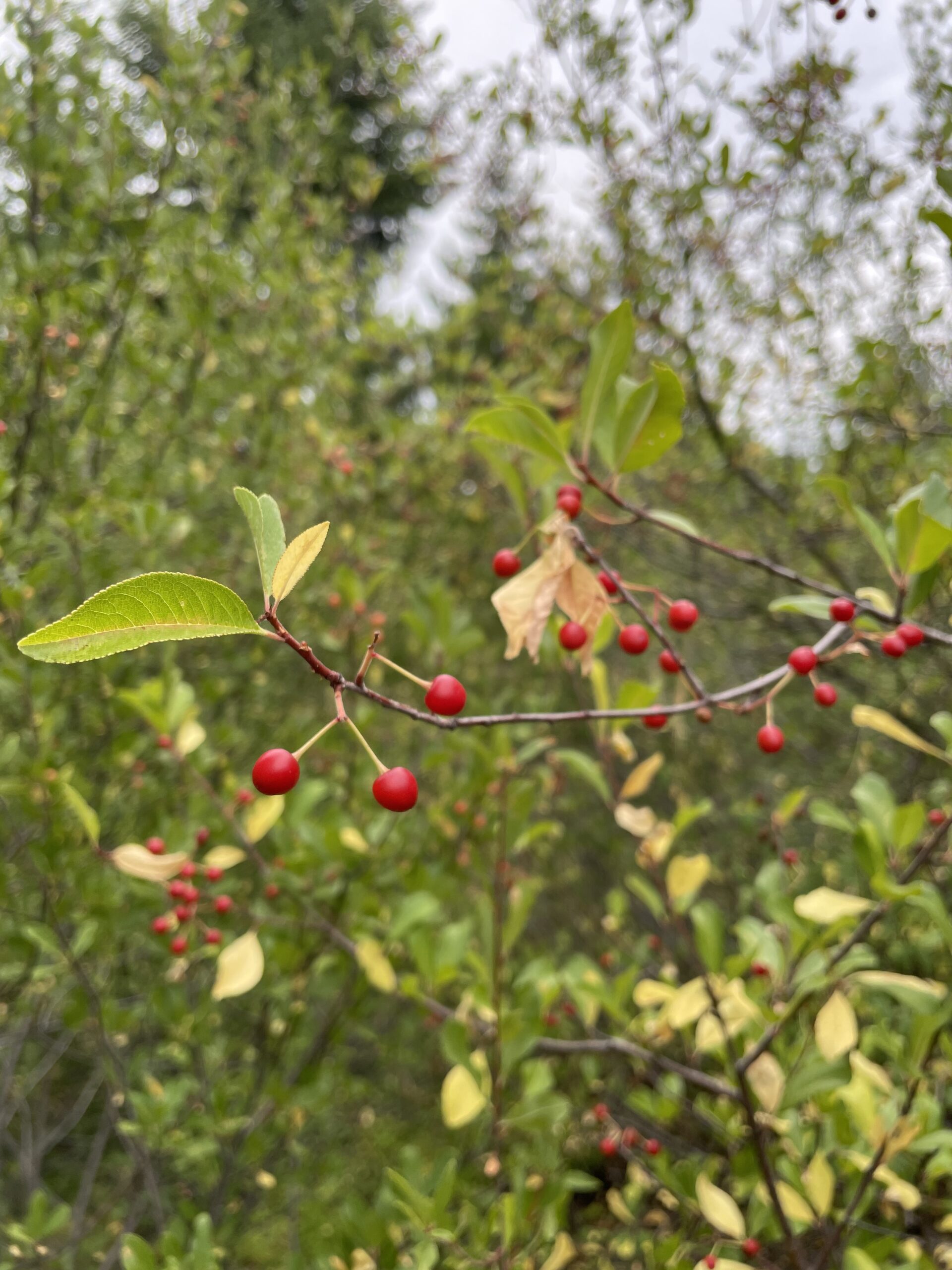


While the crew and I were busy making collections for CBG during the week, I was able to spend a few weekends picking fruits for myself! Earlier in the season I spent a day collecting some of the smaller, native blackberries located in the Forest. I cooked them down that same day, making a syrup for easy storage. This past weekend I finally got my hands on some pectin, took my stored blackberry syrup, and made jelly! While picking enough of the smaller blackberries to make jelly was a labor of love, it was absolutely worth it! I can now take a little taste of Oregon back home with me to Alabama.
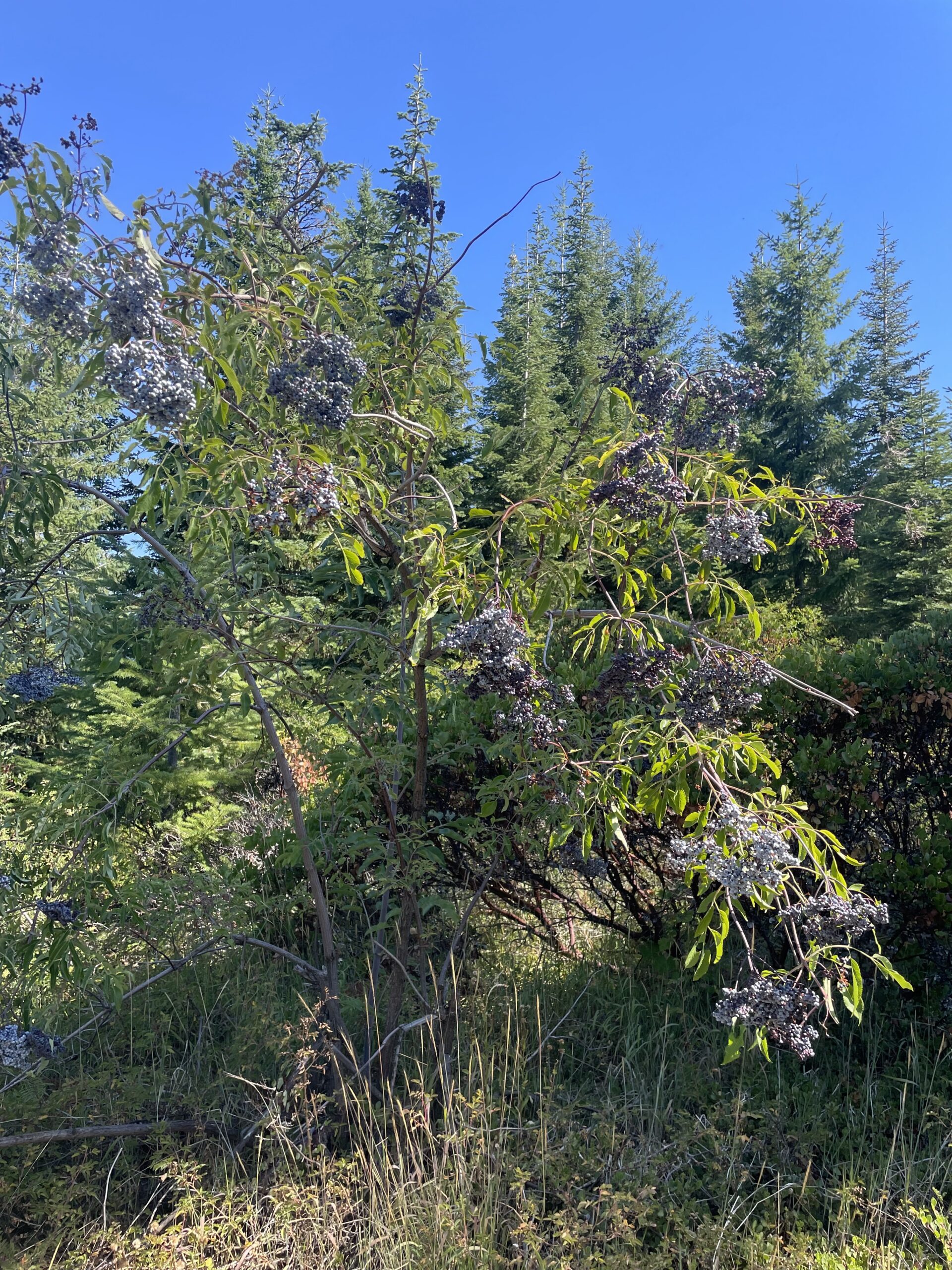
Additionally, I foraged for elderberries and also made a nice elderberry syrup with local honey in preparation for the colder months. (Just in time too! The high for Toketee this week is a rainy 53degrees. Brrrrr.) In recent years, elderberry syrup has gained popularity. These days, you can find it in just about any grocery store or pharmacy. However, elderberry syrup has been used in folk medication for hundreds of years! The syrup is known and still used today as a strong cold preventative and remedy. One cup of berries contains around 58% of the recommended daily value of vitamin C. Similar to blueberries, elderberries are also a great source of antioxidants.
Below I have the recipes I used to make my elderberry syrup!
Elderberry Syrup
Ingredients Needed (1 Batch)
- 3/4 cup of dried Elderberries – I picked my own but you can order dehydrated elderberries online. https://www.amazon.com/Elderberries-Packaging-Resealable-non-irradiated-Elderberry/dp/B09RTPRPMC/ref=sr_1_2_sspa?crid=23GS8ZXA06BAY&keywords=dried+elderberries&qid=1695657085&rdc=1&s=hpc&sprefix=dried+elder%2Chpc%2C176&sr=1-2-spons&sp_csd=d2lkZ2V0TmFtZT1zcF9hdGY&psc=1
- 1 cup of Raw Local Honey – Honey that has been filtered goes through a heating and cooling process. A majority of the enzymes, vitamins, minerals, and amino acids are killed by the high heat, negating many of the health advantages of raw honey. Additionally, raw, local honey can also shield you from seasonal allergies by gradually exposing you to local pollens until you become used to them.
- 2-3 Cinnamon Sticks (Optional)
- 2 tablespoons of shredded Fresh Ginger (Optional)
- 1 teaspoon of ground Cloves (Optional)
- 1/2 cup of dried Rose Hips (Optional)
- 3 1/2 cups of Water – I used filtered water
Equipment Needed
- Cheesecloth, small mesh colander, and/or juicer
- Saucepan
- Spoon or masher
- Container/jar for storage
- With the exception of the honey, combine all the ingredients in a heavy-bottomed saucepan and heat to a rolling boil. For my syrup, I only added shredded ginger root and cinnamon sticks.
- When the boil starts, reduce the heat to a simmer. Continue to simmer for 45 minutes stirring occasionally.
- Turn off the heat and allow the product to cool for about 30 minutes before handling it.
- Take out the cinnamon sticks and use a spoon or masher to crush the mixture.
- Squeeze through cheesecloth or pass through a fine mesh filter.
- Add 1 cup of honey to the juice it produces.
- For up to a few months, keep in the refrigerator in an airtight container. Take a teaspoon per day or as desired. I usually take 4-5 spoonfuls a week!
*Elderberry syrup is not a guaranteed “cure all”. I believe that paired with a healthy lifestyle it does boost your immune system and when taken early enough, can reduce the symptoms of a cold! With any folk or traditional medicine, appropriate expectations are required. Again, if you are eating McDonalds everyday, never engaging in any forms of exercise, stay chronically dehydrated, get terrible rest, etc. then yes, I doubt a homemade remedy will help you.