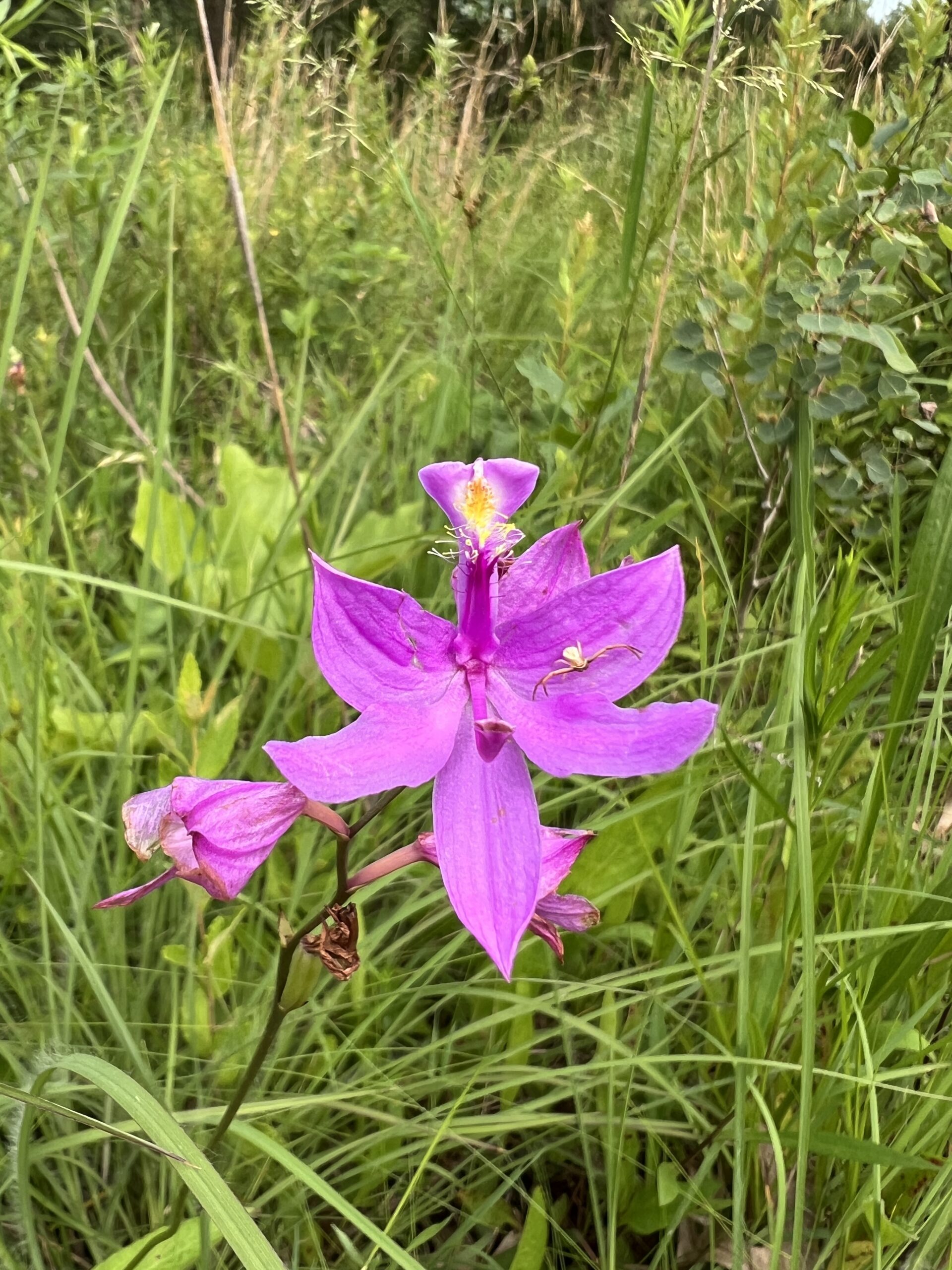
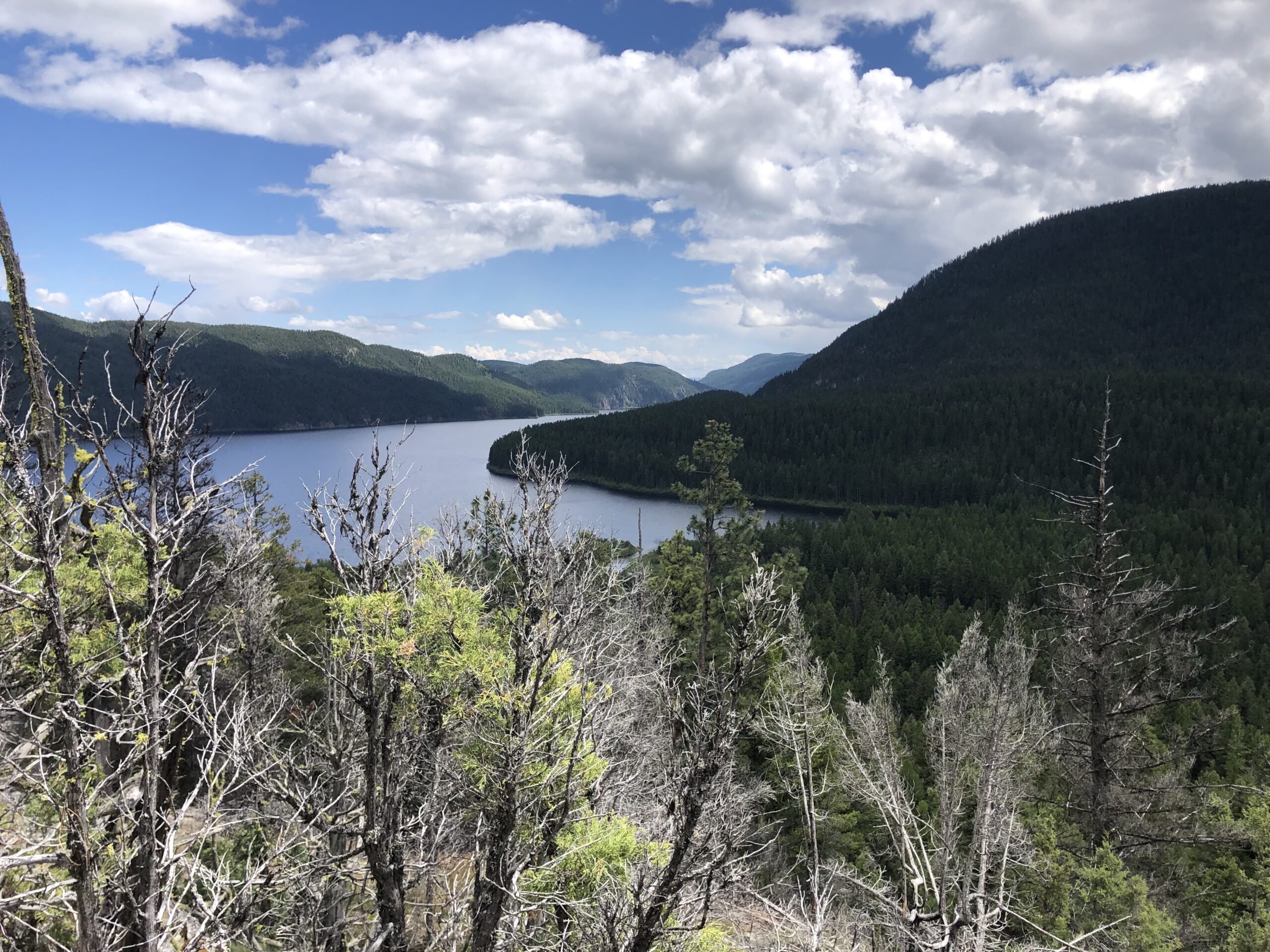
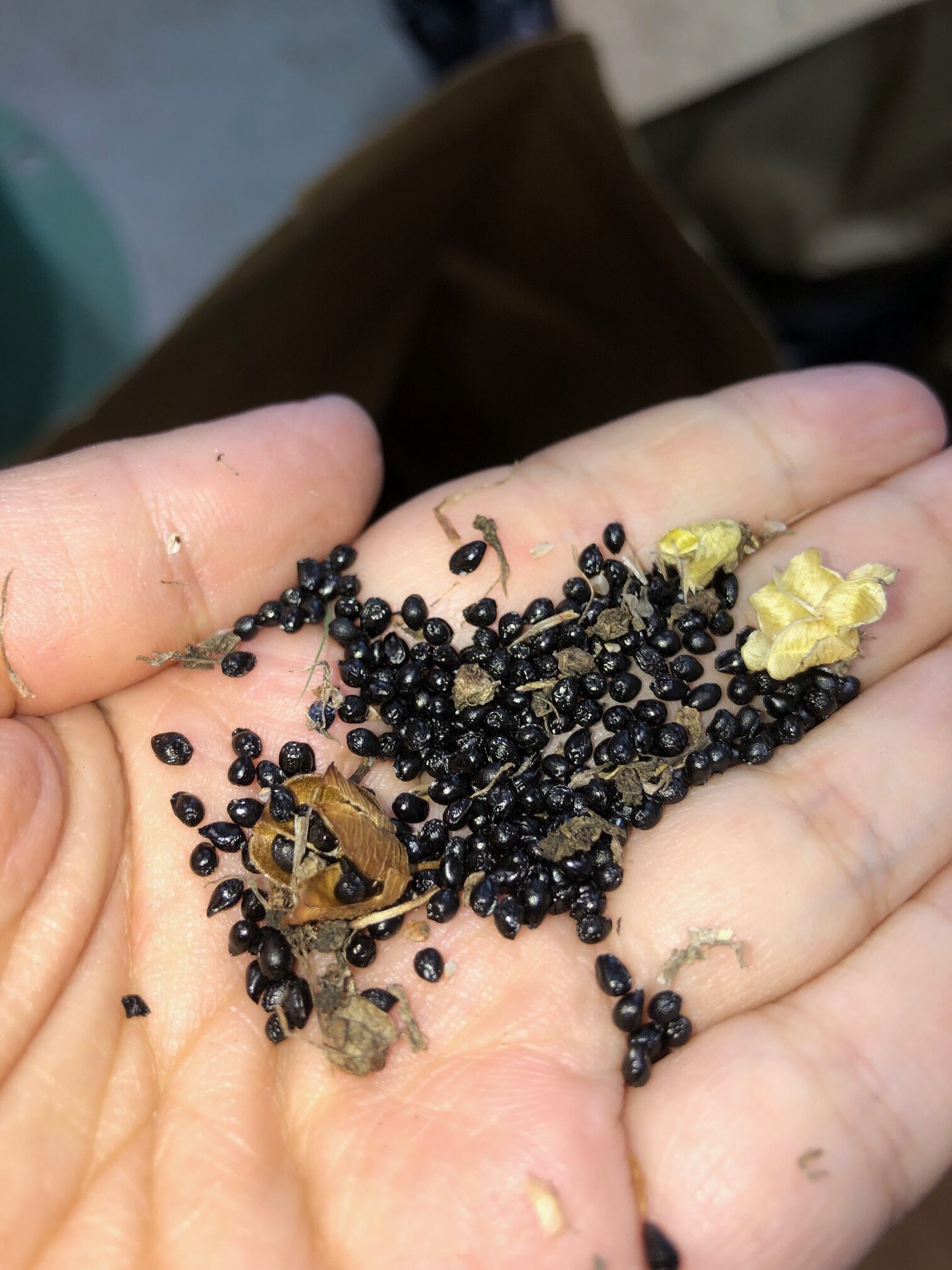
Beginning work on a new project can be intimidating. Whether it is learning the rhythm of a new team, the native species in a new region, or just finding the right folks you need to talk to in a new office. However, that was far from the case beginning my work here at the San Bernardino National Forest (SBNF).
Day #1
My first week at the SBNF involved working alongside members from the Wilderness Volunteers, an organization providing volunteer opportunities to conserve America’s wild lands through collaboration with the US Forest Service, National Park Service, the BLM, US Fish & Wildlife, and others. It was, in my opinion, an excellent introduction as I was able to learn alongside the volunteers some of the processes involved in greenhouse management and restoration site maintenance. Myself, and the volunteers, got to see the journey native plants take as they transition from seed, to small yellow bullet nursery pots, to larger black bullet nursery pots, and eventually to outplants that are used in re-vegetating sites throughout the SBNF with the aim of establishing native populations in fire scar areas as well as areas degraded by invasive species and unauthorized OHV (off-highway vehicle) usage. I felt like I was watching the process through similar eyes as the volunteers; fascinated by California’s diverse and beautiful native species as well as the highly controlled protocols followed by the SBNF when growing and handling them. These strategies are in place to prevent the spread of the water-borne pathogen Phytophthora (responsible for root rot and other nasty plant infections) from the greenhouse to the wild populations we aim to protect and restore. Some of the species we handled on that first day in the greenhouse include: Rubber rabbitbrush (Ericameria nauseosa), Big sagebrush (Artemisia tridentata), and Scarlet bugler (Penstemon centranthifolius).
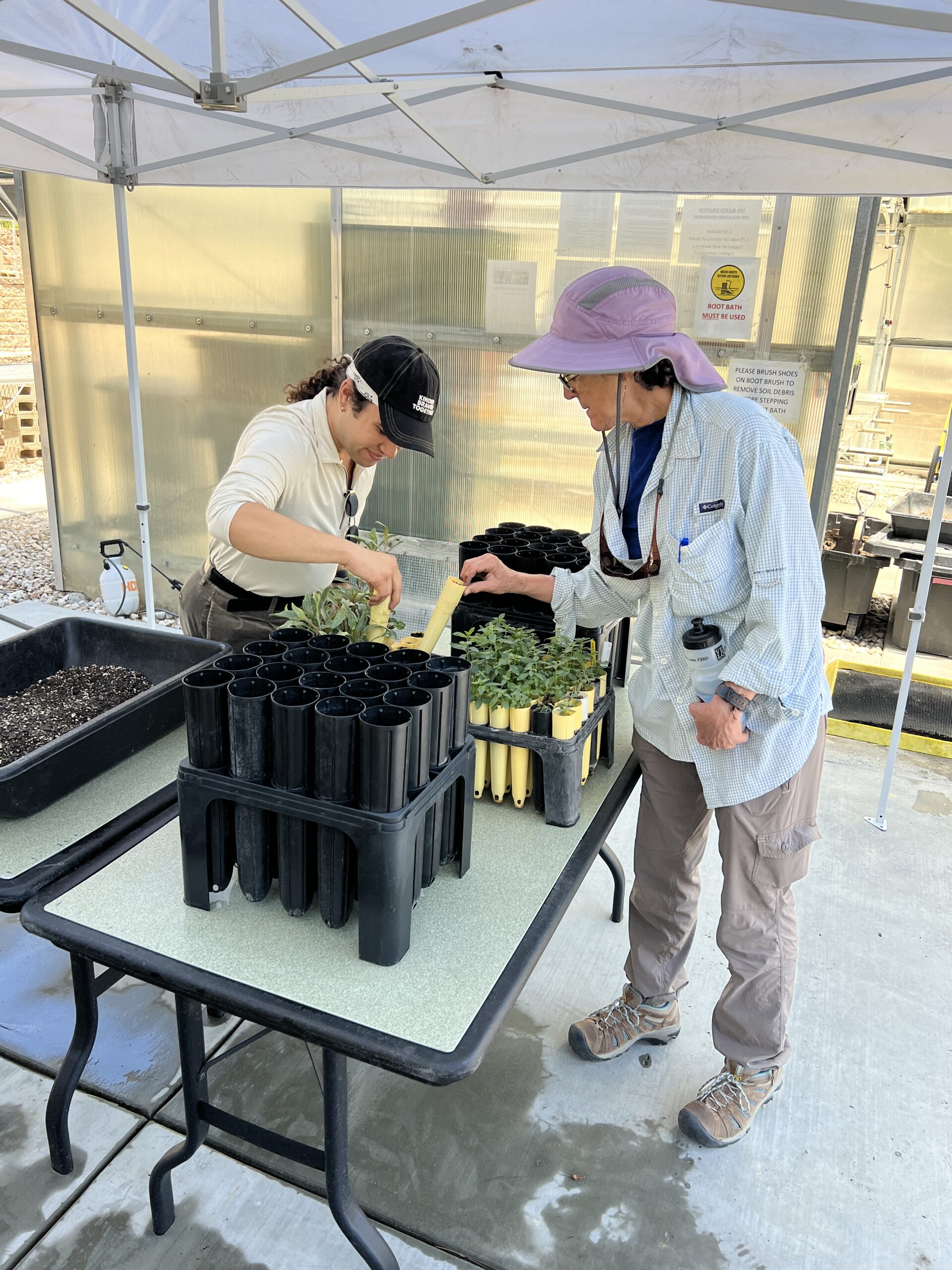

Day #2
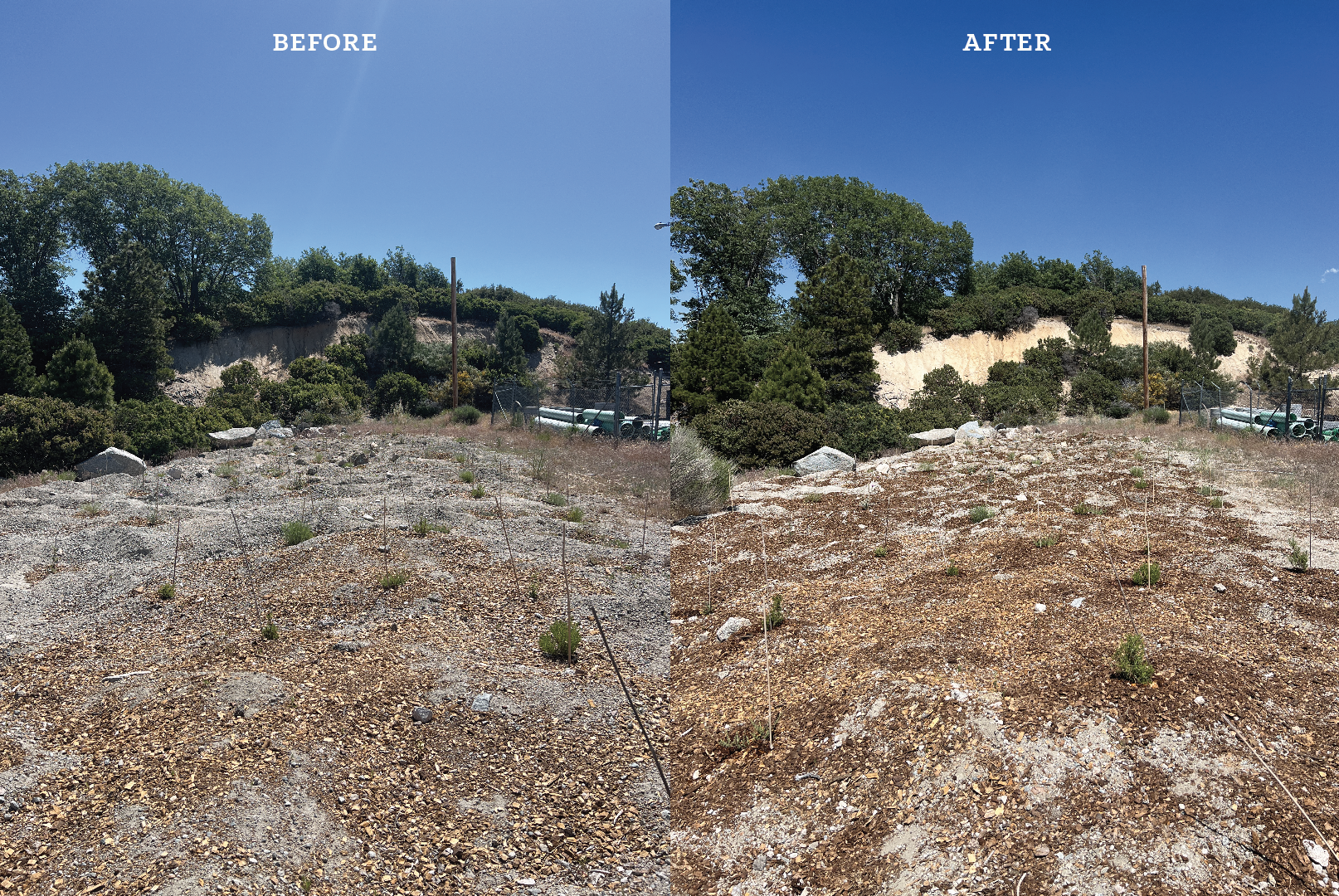
After spending day #1 getting our fingers dirty in sterile potting soil, day #2 and day #3 had us trek to actual restoration sites in the SBNF. Both sites were located near my new home away from home, one of the Forest Service cabins in Lake Arrowhead, CA. Therefore, I got to start my days with a short morning walk through the Manzanitas and yellow pines from the cabin to our nearby designated meeting point where we touched base before beginning the days work. After discussing our given restoration tasks (weeding, mulching, and watering) we took a short hike through some of the tall invasive cheatgrass surrounding the camp site until we reached our destination, a small plot of land tucked in right next to the local water treatment facility. That first day was HOT (one of the many joys of summer field work in Southern California) so it was amazing to see what good spirits the Wilderness Volunteers were in despite the harsh working conditions. We spent an hour or so weeding some of the invasive grasses and weeds that began to establish in the empty areas of the site. I even got the chance to take a few swings at using a root wrench to pull out the deep tap roots of large established Scotch Broom shrubs (Cytisus scoparius)! Some of those swings were successful and others were less so, but it was a great experience in team building and utilizing different peoples skill sets to achieve a common goal. After weeding there was mulch to be spread in order to prevent new invaders from colonizing the open ground remaining between the native outplants. We spread a LOT of mulch (approximately 8.5 yds3) using wheelbarrows and 5-gallon buckets to transport our precious cargo from the large mulch pile to areas of the site where it would be spread evenly. Throughout this process I could hear the sounds of curious volunteers asking about different native species, noticing a random wildflower, or even a butterfly dancing in the light breeze. At one point we even found a stow away western toad in our mulch pile! I enjoyed watching the ground cover transition from small patches of light brown with grayish-tan sections of open soil to a vast field of rich pine brown dotted with the beautiful light gray-ish green of many of California’s native plants throughout.

Day #3
Day #3 with the volunteers was much the same as day #2 as we conducted similar restoration site maintenance at two additional sites around Lake Arrowhead, CA. These sites were bordered with large monocultures of Mountain Whitethorn (Ceanothus cordulatus), a native species which highlighted that not all natives are good for increasing biodiversity. Ceanothus is highly adapted to fire and thrives in disturbed areas with open canopy colonizing these areas and ultimately crowding out any other native shrubs, trees, or herbaceous plants from gaining a foothold post-wildfire. In addition to the ecological war for space waging at its border, this site had another unique challenge due to the plants being out-planted onto a hillside. This made moving mulch and water up to each of the plants a bit more laborious but just as with Day #2’s heat, the volunteers handled the harsh field conditions with a positive spirit that really had a way of rubbing off onto me and lifting my spirits in general. There is nothing like struggling a bit with a team to bring people together! Combining our brains and brawn together we decided the most efficient way of moving heavy buckets full of water and mulch up the hillside would be through forming a human chain and passing buckets from one person to the next so each of us only had to cover a short distance. This technique worked so well we were able to complete these sites and still maintain smiles on all our faces when we posed for a final group photo to commemorate the days work.
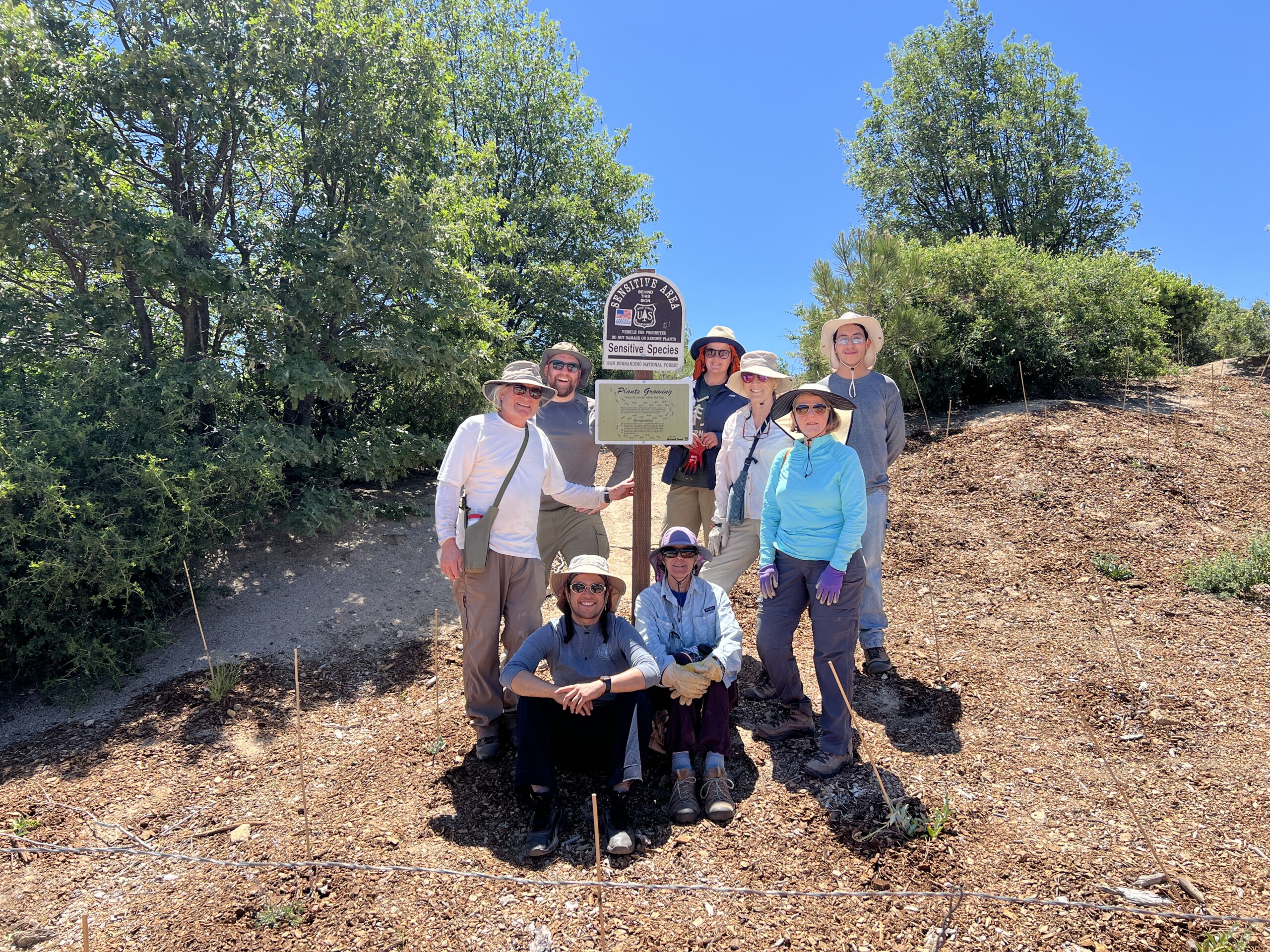

The unknowns of new beginnings can be intimidating, however working alongside all the folks at the SBNF as well as the volunteers who generously offered their time and energy for the sake of preserving native habitat truly made me feel welcomed and inspired! In total during my first week I assisted in using 1200 gal of water on outplants, maintaining 1 acre of restoration sites, and transplanting approximately 320 plants in the greenhouse here at the SBNF. None of this work could be completed alone, and I cannot wait for what the rest of this season has in store for myself, and this team!